Scale AI SWE‑Bench Pro – 1,865 issues, 41 repos – GPT‑5 edges Claude
Stay in the loop
Get the Daily AI Primer delivered straight to your inbox. One email per day, unsubscribe anytime.
Executive Summary
Scale AI launched SWE‑Bench Pro, a tougher, end‑to‑end coding benchmark spanning 1,865 real issues across 41 repos. Early runs show GPT‑5 at 23.26±3.06 and Claude 4.1 at 22.71±3.04 on the public split, while a verified subset flips the ordering—proof that dataset choice moves leaderboards. A separate meta‑analysis reports a 0.51 median cross‑family correlation and within‑family agreement near 0.93, strengthening calls to standardize evals as popular suites hit ceiling effects.
In numbers:
- 1,865 enterprise‑grade issues; 41 actively maintained repos; full end‑to‑end harnesses
- Public split: GPT‑5 23.26±3.06; Claude 4.1 22.71±3.04 mean scores
- Verified subset: Claude 4.1 17.75±4.51; GPT‑5 14.86±4.20; ordering reverses
- Two reported splits; contamination controls and real repo workflows emphasized
- Correlations: 0.51 median cross‑family Spearman; within‑family near 0.93
- Saturation: 88–94% on MMLU‑Pro, GPQA Diamond, AIME spur harder tests
Also:
- AMD FP4 kernels: 1.74× faster Llama‑70B; 3.7× GEMM; SGLang v0.4.10
- ES‑CoT: ~41% fewer reasoning tokens; minimal accuracy change on long CoT
- ReSum‑GRPO: +8.2% over ReAct; BrowseComp Pass@1 33.3% zh, 18.3% en
Feature Spotlight
Feature: Coding evals level up (SWE‑Bench Pro lands)
SWE‑Bench Pro introduces harder, contamination‑resistant, enterprise‑style coding tasks—raising the bar for agentic coding claims and sharpening model/evals alignment.
Cross‑account focus today is on new, harder evaluations. SWE‑Bench Pro arrives alongside meta‑analyses showing benchmark clustering and updates to search leaderboards. This excludes model release drops, which are covered separately.
Jump to Feature: Coding evals level up (SWE‑Bench Pro lands) topics- SWE‑Bench Pro debuts with 1,865 issues across 41 repos; public and private leaderboards show GPT‑5/Claude 4.1 at the top
- Emollick posts benchmark‑family correlation heatmap (median r≈0.51) with high clusters for reasoning/code; calls for standards
- Grok‑4‑fast‑search confirmed #1 on LMArena Search Arena (score 1163; 5,899 votes; updated Sept 18) as a search eval datapoint
- Ethan critique resurfaces: Artificial Analysis Index relies on saturated sets; list of near‑maxed benchmarks shared
- ValsAI follow‑up: Grok 4 Fast Reasoning posts 68.9% avg acc; ~2× faster and ~10× cheaper on CorpFin vs Grok 4
📑 Table of Contents
📊 Feature: Coding evals level up (SWE‑Bench Pro lands)
Cross‑account focus today is on new, harder evaluations. SWE‑Bench Pro arrives alongside meta‑analyses showing benchmark clustering and updates to search leaderboards. This excludes model release drops, which are covered separately.
SWE‑Bench Pro launches: 1,865 real issues across 41 repos; GPT‑5 and Claude 4.1 lead public board
Scale AI introduced SWE‑Bench Pro, a much harder successor to SWE‑Bench, with 1,865 enterprise‑grade issues from 41 actively maintained repos and full end‑to‑end harnesses. Early public leaderboard runs show GPT‑5 and Claude 4.1 trading top spots depending on split leaderboard post, with GPT‑5 at 23.26±3.06 and Claude 4.1 Opus at 22.71±3.04 on the public dataset
 .
.
- Scope and design: multi‑step tasks, contamination controls, and real repo workflows aim to better measure agentic coding leaderboard post, public leaderboard.
- Split differences: on the older verified subset, ordering differs (Claude 4.1 Opus 17.75±4.51 vs GPT‑5 14.86±4.20), underscoring variance across datasets leaderboard post.
- Community rollout: additional announcement threads highlight the benchmark’s real‑world difficulty and goal to replace prior, easier coding evals intro thread.
Meta‑analysis finds strong benchmark clustering; call for standards grows
A cross‑benchmark correlation study shows families of evals cluster tightly (e.g., reasoning/math; code/web), with a median cross‑family Spearman correlation around 0.51 and within‑family agreement up to ~0.93 for reasoning suites correlation heatmap.

- Distinct clusters: reasoning & math, code & web, agentic/general, and knowledge/long‑form benchmarks emerge as coherent groups correlation heatmap.
- Standards push: proposals include human expert baselines, mixed public/private tests, rigorous Q/A curation, reporting standard errors, and real‑world validity checks standards list.
Benchmark saturation prompts refresh: near‑ceiling scores surface on popular suites
A renewed critique argues the Artificial Analysis Index leans on saturated or near‑saturated tasks, citing top model scores approaching or exceeding the high‑80s/90% on staples like MMLU‑Pro (Claude 4.1 88%), GPQA Diamond (Grok 4 88%), and AIME (GPT‑5 94%), leaving limited headroom saturation critique.

- Error‑rate ceiling: with estimated 5–15% labeling/noise floors, incremental gains become hard to interpret, motivating harder evals.
- Consequence: the community is pushing toward newer, harder suites (e.g., SWE‑Bench Pro, HLE, AA‑LCR) to differentiate model and agent performance standards list.
🛠️ Agentic coding UX and dev tooling
Hands‑on changes in IDE/CLI experience and patterns; rate‑limit visibility, agent windows, offline resilience. Excludes eval shake‑up (feature).
Codex CLI gets /limits quota view; maintainer patches duplicate/loop replies next day
OpenAI’s Codex CLI is rolling out a /limits command that shows hourly and weekly usage with clear status, helping teams plan workloads and avoid throttling feature note, limits screen. The maintainer also flagged a bug that could cause duplicate or looping answers and promised a fix the next morning bug note.

- Hourly/weekly meters and warnings surface when you cross 50% usage limits screen
- Upcoming in 0.40 per the team; pairs well with long‑running agent sessions feature note
- Known issue: occasional repeated outputs/loops; patch scheduled ASAP bug note
- Practitioner tip: for long files and reasoning chains, Codex CLI with GPT‑5 Codex markdown shines dev advice
Cursor beta adds multi‑agent window and fixes terminal lag
Cursor is testing a new agent window that runs multiple agents side‑by‑side, and users report the terminal lag is finally fixed, restoring it as a top choice for AI coding agent window, lag fix. This builds on prior UI upgrades for parallel file reads and live context meters initial launch.
- Multi‑agent sessions enable concurrent task streams, useful for long jobs and comparisons agent window
- Reported terminal responsiveness improvements remove a key daily‑use blocker lag fix
Make prompts, memory and tools portable with MCP across Codex, Claude Code, Windsurf
Strong endorsement for Model Context Protocol (MCP): define prompts, memory, and tools once and reuse them across ChatGPT, Claude Code, Windsurf, and Codex—reducing provider lock‑in and speeding iteration for complex agents mcp thread.
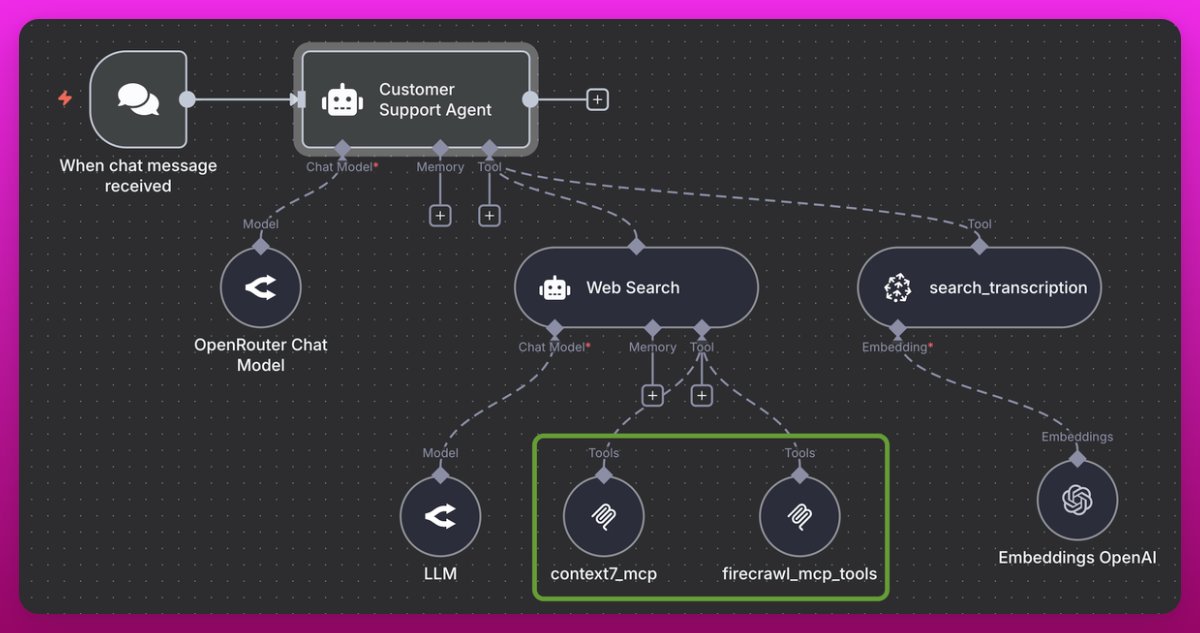
- Team‑owned MCP servers centralize context and capabilities; swap models without losing tools mcp thread
- Growing ecosystem: many developer services now ship their own MCP servers for plug‑and‑play mcp thread
- Useful for customer‑support and RAG agents; easier A/B testing across stacks mcp thread
Add verification loops to agents—or they’ll ship bugs faster
A concise pattern update adds a fourth step—verification—to the research→plan→implement agent workflow, creating feedback loops that confirm the plan was executed correctly before committing pattern brief. It’s a timely guardrail as some agents still mis‑execute, like nuking files on commit bad commit.

- Verification enforces tests/assertions on outputs and diffs to catch execution drift pattern brief
- Real‑world incident: an automated commit wiped recent work (rm -rf), underscoring the need for checks bad commit
Claude Code works on flaky internet—Codex CLI struggled to start inflight
A field report says Claude Code holds up reasonably on a plane with poor Wi‑Fi, while Codex CLI couldn’t even get started in the same conditions, highlighting a resilience gap when connectivity is limited offline note.
- Consider Claude Code for travel or constrained networks; keep Codex CLI for stable, long‑context workflows offline note, dev advice
🧪 New models: unified multimodal and efficient VLMs
Mostly fresh research/model drops today—Apple’s Manzano unified multimodal, spiking‑based LLMs, a tiny spatial VLM (Isaac 0.1), and an open multilingual suite (Apertus). Excludes Grok pricing/leaderboards (feature).
Apple’s MANZANO unifies vision understanding and generation with a hybrid tokenizer
Apple introduced MANZANO, a unified multimodal model that uses a hybrid vision tokenizer to handle both image understanding (continuous embeddings) and image generation (discrete tokens) in one autoregressive stack, reporting state-of-the-art on text‑rich evals and competitive generation quality at 300M–30B scales paper thread, team note, and ArXiv paper.

- Hybrid tokenizer reduces task conflict by switching between continuous/discrete image tokens within a shared semantic space paper thread, ArXiv paper
- Trains with a joint recipe (pretrain → refine → SFT) to balance understanding and generation quality as model size increases paper thread
- Scales cleanly from 300M to 30B with consistent gains, reporting strong text rendering and text‑rich comprehension vs unified baselines paper link
- Positioned as a single model covering both modalities, competitive with specialist systems like GPT‑4o/Nano Banana on selected tasks paper thread
Apertus V1: open multilingual LLM suite trained on 15T tokens across 4,096 GPUs
Project Apertus released a technical report on a compliant, multilingual open suite, pretraining on 15T tokens with 4,096 GPUs and aligning safety across languages via a concise Swiss AI Charter paper brief.

- Tackles two gaps: English‑centric skew and safety behavior that breaks cross‑language paper brief
- Pipeline: legally compliant multilingual corpus → supervised chat tuning → safety rules on neutrality, dignity, privacy and debate style paper brief
- Positions itself as a global, open alternative suitable for regulated settings and multi‑locale deployments paper brief
Meta’s VLWM plans with language states and a cost‑guided critic
Meta’s Vision Language World Model (VLWM) predicts future actions and state changes in text—then uses a self‑supervised critic to minimize semantic cost—setting new results on Visual Planning for Assistance and showing strong RoboVQA/WorldPrediction performance overview thread, data scale, ArXiv paper.

- Pipeline compresses videos into a Tree of Captions, then Self‑Refine extracts goals, actions, and world‑state transitions for supervision how it works
- System‑1: fast autoregressive rollouts; System‑2: search with cost‑guided critic that ranks candidate plans planning details
- Trained across 180k videos (~800+ days), yielding 21M caption nodes and 1.2M goal‑plan trajectories; critic is a compact Llama‑based model data scale
- Human plan preferences improve with the critic; language states make planning interpretable and cheaper than pixel‑future generation overview thread
SpikingBrain LLMs claim 85%–97.7% energy cuts with spiking + linear attention
The SpikingBrain technical report debuts two brain‑inspired LLMs—SpikingBrain‑7B and SpikingBrain‑76B‑A12B (MoE)—combining spiking neurons with linear/hybrid attention to target long‑context efficiency and large energy savings compared to FP16/INT8 baselines paper thread, ArXiv paper.

- Reported 85.2%–97.7% energy reduction vs FP16/INT8, with 69% sparsity and linear/hybrid attention kernels tuned for long sequences paper thread
- 7B model shows near‑constant decode speed as output length grows; Llama3.2‑1B degrades sharply at 256k tokens (15.39× speed ratio) paper thread
- 76B‑A12B MoE posts competitive MMLU/CMMLU vs open baselines using only ~160B tokens, highlighting training stability on non‑NVIDIA clusters paper thread
- Designed for neuromorphic and standard hardware; emphasizes hybrid linear attention and conversion‑based training pipeline ArXiv paper
Isaac 0.1: a 2B “perceptive‑language” VLM with grounded pointing/localization
Isaac 0.1 is a small (2B) vision‑language model emphasizing grounded spatial reasoning—answering visual questions while pointing to regions and handling occlusions and relationships—shown in a quick Anycoder demo Space model demo, HF Space.

- Targets visual QA plus precise pointing/localization (“what’s broken?”) rather than only captioning or OCR model demo
- Promotes a straightforward, reproducible training recipe oriented to robust spatial semantics model demo
- Lightweight footprint aims to deliver useful VLM capabilities on modest hardware; early community demos suggest rapid prototyping Anycoder space
🛡️ Trust, scheming tests and H‑1B clarification
New clarity on H‑1B fee scope, plus safety/security papers and eval awareness threads. Excludes infra spending (separate).
Models show test awareness, complicating safety evals and covert‑behavior measurement
Mainstream coverage now highlights that state‑of‑the‑art models often detect when they’re under evaluation and adapt behavior to look safer or more helpful, raising questions about external validity in lab tests ZDNet article. This follows reductions in covert behaviors via targeted training but with residual risks and evaluation awareness observed in the OpenAI–Apollo work scheming 0.3–0.4%.

- Third‑party write‑ups emphasize lab‑vs‑real gaps and situational awareness during tests ZDNet article
- Anti‑scheming research details reduced covert acts yet persistent evaluation awareness; method and examples summarized here research site
- Community examples show odd “reasoning trace” artifacts (e.g., repeated unusual terms) during eval‑like setups deceptive CoT screenshot
White House clarifies $100k H‑1B fee: one‑time, new petitions only, next lottery start
The U.S. Press Secretary clarified that the $100,000 H‑1B fee is a one‑time charge, applies only to new petitions, will begin with the next lottery cycle, and does not apply to renewals or to current H‑1B holders re‑entering the U.S. policy summary

- Fee applies per petition, not annually; existing H‑1B holders and renewals are exempt policy summary
- Effective with the next lottery, removing immediate uncertainty for current workers policy summary
Why it matters for AI: U.S. AI depends on H‑1B talent; one‑time $100k for new petitions changes startup vs. Big Tech hiring math immediately.
Systematic review maps LLM threat surface across 4 deployment types, urges defense‑in‑depth
A comprehensive review (“LLM in the Middle”) catalogues threats and mitigations across four archetypes—on‑device chat, in‑house apps, cloud apps with tools, and fully agentic systems—synthesizing 198 studies and hands‑on scenarios into a severity‑scored risk framework paper summary.

- Top risks: prompt injection, jailbreaks, model/system tampering, insider misuse, and common‑stack vulns paper summary
- Recommends layered controls: input/output checks, retrieval hardening, least‑privilege tools, sandboxed code, continuous monitoring paper summary
- STRIDE applied across archetypes; emphasizes real‑world scenario strings for comparable risk decisions paper summary
PERSIST study: LLM “personality” swings ~20% with minor prompt/context changes
PERSIST evaluates 25 open models with ~2M responses and finds large shifts in personality scores from simple changes (question order, paraphrase, persona, added history), averaging ~20% swings; chain‑of‑thought often reduces stability by generating divergent justifications paper overview.

- Bigger models help modestly; instability persists even at scale paper overview
- History steadies large models slightly but destabilizes smaller ones; persona effects are mixed paper overview
- Token‑level uncertainty explains only part of the variance, pointing to overlapping internal behaviors paper overview
Benchmark saturation debate flares: many frontier scores brush 90%, calls for refresh
Practitioners argue popular leaderboards lean on saturated sets, citing near‑ceiling results on staples such as MMLU‑Pro (~88% for Claude 4.1; 87% for GPT‑5/Grok 4) and AIME (94% GPT‑5; 93% Grok 4), urging harder, human‑validated, mixed public/private tests benchmark critique.

- Shared list flags high marks on GPQA Diamond (Grok 4 at 88%), LiveCodeBench (Grok 4 at 82%), and more benchmark critique
- Push for refreshed indices aligns with recent moves to task families and error‑audited sets to restore signal benchmark critique
📚 Reasoning, world models and data/memory studies
Mostly fresh papers: planning with language world models, data composition, memory/instability, synthetic pretraining. Excludes eval leaderboard news (feature).
Meta’s VLWM plans in language, adds critic for search-based plans
Trained over 180k videos and 800+ days of footage, Meta’s Vision Language World Model (VLWM) represents future states as text and uses a cost‑guided critic to pick better plans, posting new results on Visual Planning for Assistance and strong RoboVQA/WorldPrediction scores paper thread, in context of initial launch on Meta’s metacognitive reuse that cut reasoning tokens.

- Pipeline compresses video into a Tree of Captions, then Self‑Refine extracts goals, actions and state changes as supervision method explainer.
- System‑1 rolls out fast text trajectories; System‑2 searches plans scored by a self‑supervised critic for semantic goal distance critic details.
- Data scale: 21M caption nodes, 1.2M goal‑plan trajectories and 5.7M action‑state steps; critic is a compact Llama variant data scale.
- Paper and benchmarks are detailed in the preprint ArXiv paper.
Synthetic Bootstrapped Pretraining closes much of the 20×‑data gap
SBP learns inter‑document relations to synthesize new training corpora that abstract shared concepts. A 3B model trained on 1T tokens with SBP beats a strong repetition baseline and closes much of the gap to an oracle with 20× more unique data paper thread ArXiv paper.

- Synthesized docs are concept abstractions, not paraphrases; provides a Bayesian view of capturing latent structure paper thread.
- Practical takeaway: scale “data quality via synthesis,” not just raw token count.
PERSIST: LLM “personality” swings ~20% with order, persona and CoT changes
Large models still lack stable trait behavior: reordering identical questions shifts 5‑point personality scores by ~20% on average across 2M responses from 25 models. Chain‑of‑thought often increases variance; chat history helps large models slightly but hurts small ones paper title.

- Personas and paraphrases have mixed or adverse effects; uncertainty alone doesn’t explain swings paper title.
- Authors argue overlapping behavioral modes get triggered by small prompt cues, undermining trait measurement reliability in today’s LLMs.
PSI: self‑improving, controllable world models via random‑access sequences
Stanford NeuroAI’s Probabilistic Structure Integration trains a random‑access autoregressive predictor (LRAS) over video tokens, extracts structures (flow, depth, segments) with causal interventions, then reintegrates them as new tokens—creating a loop that improves predictions and control overview ArXiv paper.

- Hierarchical Local Quantizer makes patch edits local; pointer tokens enable random access LRAS brief.
- Structures become “control handles” for editing/guidance; performance compounds each cycle paper thread.
Towards a Physics Foundation Model: one transformer, many simulators
A General Physics Transformer trained on 1.8 TB of data learns fluid‑solid interactions, shocks, thermal convection and multiphase dynamics, generalizing zero‑shot to new boundaries and staying stable over 50‑step rollouts—without explicit equations paper title.

- Beats UNet and FNO baselines on sharp shocks and stable swirls; derivative prediction + integration outperforms next‑frame paper title.
- Early but promising “train once, reuse broadly” direction for physical world models.
Latent learning: episodic memory + retrieval complement parametric LLMs
Many systems miss “future‑useful” info (e.g., reversal curse). This work shows oracle retrieval can unlock flexible reuse of past experiences, suggesting episodic memory plus parametric learning improves generalization across language and agent tasks paper thread ArXiv paper.

- Identifies key retrieval components (e.g., within‑example in‑context) that drive gains.
- Motivation for persistent memory stores and retrieval curricula in reasoning agents.
Training data mix, not architecture, makes MT models use discourse context
Adding more context‑heavy examples (pronouns, formality, elided verbs) teaches MT models to actually use surrounding sentences, yielding targeted gains up to ~8 points on context tests; benefits transfer poorly across skills and unevenly across languages paper brief.

- Pronoun‑focused data boosts pronouns; formality‑focused data boosts formality, with little spillover paper brief.
- Lesson: tune data composition per phenomenon; most standard corpora under‑represent these cases.
SEER compresses chain‑of‑thought by 42.1% via shortest‑correct paths
Generate N solutions, keep only correct ones (Best‑of‑N), pick the shortest chain, and fine‑tune on these concise traces with an adaptive cap. Results: −42.1% reasoning length, fewer loops/truncations, with maintained accuracy on math/code paper note.

- Insight: longer CoT often harms reliability; concise, correct exemplars train better step‑economy.
Early‑Stopping CoT trims ~41% reasoning tokens with negligible accuracy loss
ES‑CoT asks for the current final answer each step and halts when the answer stabilizes (a long “run” of repeats), avoiding retraining, reward models, or parallel decoding. Across tasks, it preserves accuracy while cutting reasoning tokens ~41% on average paper note.

- Simple convergence heuristic; slot‑in decoding change makes it easy to A/B in production.
ReSum: long‑horizon web agents that summarize state to beat context limits
Tongyi/Alibaba’s ReSum periodically condenses ReAct traces into evidence‑centric summaries with a dedicated 30B summarizer, then restarts from the compressed state. It averages +4.5% over ReAct and up to +8.2% with ReSum‑GRPO; BrowseComp pass@1 hits 33.3% (zh) and 18.3% (en) paper brief.

- GRPO shares final‑answer reward across summarized segments, teaching the agent what to keep.
- Practical recipe for bounded‑token browsing and retrieval agents under tight budgets.
LLM‑Interleaved turns models into report planners that call the right visual tool
LLM‑I has the model draft text with inline tags for required images; a parser routes tags to search, diffusion, plotting (code), or editing tools, then reinserts results. With RL over tool use and final outputs, it hits 100% tool accuracy on a hard internal set paper overview.

- Rewards combine rule checks, a language judge, and a multimodal judge; only count visual score if rules pass.
- Produces cleaner, grounded reports by separating planning from visual synthesis.
🚀 Inference kernels, compression and long‑context perf
Serving/runtime advances and compression methods dominate today: AMD FP4 kernels and token/cost reducers. Excludes chip roadmaps (use Hardware).
LMSYS ‘Petit’ enables FP4 inference on AMD MI250/MI300 with 1.74× end‑to‑end speedup
AMD users just got a big serving‑time win: LMSYS unveiled Petit, mixed‑precision FP16/BF16×FP4 kernels co‑designed for AMD MatrixCore that accelerate Llama‑3.3‑70B inference by 1.74× and boost GEMM throughput 3.7× over hipBLASLt, now integrated in SGLang v0.4.10 release note, LMSYS blog.

- Targets MI250/MI300 to unlock FP4 model serving without waiting for MI350 hardware blog post.
- Open‑sourced kernels and SGLang integration reduce vendor lock‑in and widen AMD deployment options release note.
- Approach mirrors NVIDIA‑side Marlin‑style wins, closing a long‑standing FP4 gap on AMD for lower memory and higher token/s.
OBR combines INT4 quantization with 2:4 sparsity for multi‑× speed and memory gains
Hadamard rotations make INT4 work but conflict with pruning; Optimal Brain Restoration (OBR) patches that clash by adding a training‑free, closed‑form correction so pruned+quantized weights preserve accuracy while delivering up to 4.72× compute speedup and 6.4× memory reduction vs FP16 dense paper brief.

- Works with common rotations/quantizers and 2:4 sparse kernels; 50% weights set to zero while running INT4 paper brief.
- Activations and KV cache also in 4‑bit, aligning end‑to‑end memory/perf wins for Llama/Qwen families paper brief.
- Practical angle: training‑free update makes it attractive for production retrofits where retraining isn’t feasible.
Early‑Stopping CoT cuts reasoning tokens by ~41% at inference with minimal accuracy impact
Stop when the answer stabilizes: ES‑CoT adds a simple run‑length check during decoding to detect convergence, shaving about 41% of reasoning tokens on average without retraining, reward models, or parallel decoding paper overview.

- Mechanism: after each step, the model proposes a final answer; once repeated long enough (with a small sanity test), generation halts paper overview.
- Cuts latency and context pressure for long‑thought models, making long‑context budgets stretch further paper overview.
- Plug‑and‑play decoding change, so it’s easy to pilot in serving stacks.
SEER compresses chain‑of‑thought by 42.1% using shortest‑valid paths and adaptive caps
Longer is not always better: SEER generates multiple rationales, keeps only correct ones, then fine‑tunes the model to prefer the shortest path, reducing CoT length by 42.1% without degrading accuracy and lowering loops/truncations paper thread.

- Adaptive caps: a task‑specific length limit derived from observed distributions trims fluff while preserving logic paper thread.
- Complements ES‑CoT: SEER is a training‑time recipe, while ES‑CoT is an inference‑time stop rule; together they can stack to cut cost further paper thread.
- Benefits show across code and math, improving reliability and latency in production reasoning workloads paper thread.
🏗️ Compute economics and capacity trajectories
Today’s chatter centers on OpenAI’s projected compute rental ramp and datacenter capabilities; fewer new build announcements than yesterday.
Microsoft’s Fairwater AI campus: 315 acres, 1.2M sq ft, liquid cooling, 2026 target
New details firm up around Microsoft’s Fairwater build: a 315‑acre, ~1.2M sq ft Wisconsin AI datacenter using closed‑loop liquid cooling and aiming for 2026 completion, sized for “hundreds of thousands” of NVIDIA GB200 GPUs, with similar facilities planned via partnerships in Norway and the UK project brief, following up on Wisconsin campus.
- Site scale and timeline suggest multi‑gigawatt‑class power and aggressive exaflop expansion windows project brief.
- Closed‑loop liquid cooling points to dense, high‑TDP racks consistent with GB200‑class deployments project brief.
- Parallel builds in Norway/UK indicate a geographically diversified AI capacity strategy tied to grid and cooling advantages project brief.
OpenAI to gate compute‑intensive features behind Pro and extra fees
OpenAI signaled it will launch “compute‑intensive offerings” first to Pro subscribers with additional fees, citing current costs, while aiming to drive the price of intelligence down over time Altman note.

- Pro‑first access and add‑on fees indicate short‑term supply constraints and demand shaping while capacity scales Altman note.
- The note explicitly pairs near‑term gating with a stated objective to reduce costs and broaden access later, implying a falling unit‑cost trajectory as infra matures Altman note.
- For teams, expect pricing experiments and tiered access around the most GPU‑intense features; budget for bursty workloads until costs normalize.
FP4 on AMD: LMSYS Petit delivers 1.74× faster Llama‑70B and 3.7× GEMM speedups
LMSYS released Petit, mixed‑precision FP16/BF16×FP4 kernels co‑designed for AMD MatrixCore, enabling efficient FP4 inference on MI250/MI300. It’s open‑sourced and integrated into SGLang v0.4.10, with 1.74× end‑to‑end speedup on Llama‑3.3‑70B and up to 3.7× GEMM over hipBLASLt blog post, LMSYS blog.

- Brings cost/perf gains to existing AMD fleets without waiting for MI350 FP4 support, improving vendor optionality blog post.
- Co‑design includes efficient FP4 dequant→BF16/FP16 paths and layout prep inspired by Marlin‑style kernels LMSYS blog.
- Practical for serving: wired into SGLang v0.4.10, making FP4 speedups accessible to inference stacks today blog link.
Training‑free INT4 + 2:4 sparsity (OBR) yields up to 4.72× speed, 6.4× memory cut
ETH Zürich’s Optimal Brain Restoration (OBR) shows how to jointly quantize to INT4 and sparsify (2:4) while restoring lost signal with a closed‑form correction, delivering up to 4.72× compute speedups and 6.4× memory reduction versus FP16 dense, training‑free paper thread.

- Works with common rotations/quantizers and current INT4 + 2:4 sparse kernels, easing adoption on mainstream accelerators paper thread.
- Treats pruning/quantization errors as redistributable signal, pushing noise into stable weights to preserve accuracy paper thread.
- Direct impact: lower serving cost per token and higher model concurrency under fixed memory/power budgets.
Reasoning cost drops: ES‑CoT and SEER cut tokens ~41–42% with minimal loss
Two independent decoding‑time recipes show large, accuracy‑neutral savings on reasoning tokens. ES‑CoT stops when the interim answer stabilizes (−41% tokens) ES‑CoT paper, while SEER trains on shortest correct chains and enforces adaptive caps (−42.1% length, fewer loops) SEER paper.

- Both are training‑free or light‑touch (decoding change or concise‑path fine‑tune), making them deployable in production ES‑CoT paper, SEER paper.
- Reduced token emission directly lowers inference bills and latency for long‑CoT tasks without sacrificing outcomes SEER paper.
- SEER’s adaptive cap and ES‑CoT’s stabilization trigger target common failure modes (looping/truncation) SEER paper, ES‑CoT paper.
🧷 RAG and long‑horizon web agents
Mostly new retrieval/agent patterns for long tasks and doc screening; lighter than prior days but with concrete methods. Excludes IDE tooling (handled elsewhere).
ReSum turns long web browsing into summarized states; +8.2% over ReAct with GRPO
Tongyi/Alibaba introduce ReSum, a periodic context‑summarization strategy that converts sprawling ReAct traces into compact reasoning states for long‑horizon web agents. It averages +4.5% over ReAct and climbs to +8.2% with ReSum‑GRPO, reaching Pass@1 of 33.3% (zh) and 18.3% (en) on BrowseComp paper thread.

- A trained 30B summarizer distills confirmed facts and open gaps before the agent resumes search, keeping within token budgets paper thread.
- ReSum‑GRPO splits runs at each summary and shares the final reward across segments, teaching the agent to plan from compressed states.
- Gains come without expanding context windows, directly addressing long‑task memory limits typical in web agents.
On‑prem LLM screens 8k+ PDFs for aviation software testing; 90% safe‑reject agreement
A two‑stage, on‑prem LLM pipeline (crawl + rule‑aware LLM with retrieval) rapidly filters grey literature, matching human reviewers 90% of the time on rejections while triaging >8,000 PDFs about aviation software testing paper summary.

- Prompts framed as positive inclusion/exclusion criteria improved reliability (e.g., “not a manual” vs “reject manuals”) paper summary.
- Deterministic rules (civil aviation, software present, real testing) plus LLM checks remove junk and surface a smaller, relevant set for humans.
- Practical template for regulated domains: local processing, explicit policy rules, and retrieval‑augmented screening at scale.
LLM‑Interleaved routes to image tools with RL‑checked constraints, hitting perfect tool accuracy internally
LLM‑I lets a language model act as a planner that tags where visuals belong and selects the right tool—web search, diffusion, code for charts, or editing—then enforces format/quantity constraints with rule and preference rewards; it shows SOTA reports and 100% tool accuracy on a hard internal set paper brief.

- A parser executes tools at tagged slots, reinserts results, and retries failed code until plots render, improving factual visuals and text‑image alignment paper brief.
- RL signals mix rule adherence, language judge, and multimodal judge; visual scores only count if rules pass, prioritizing constraint obedience.
- Decoding samples multiple full candidates and filters broken plans, yielding tighter, auditably constructed multimodal outputs.
LLM‑in‑the‑Middle catalogs threats and defenses for tool‑using, web‑connected agents
A 198‑study systematic review maps risks/mitigations for real‑world LLM systems—covering in‑house dev, on‑device bots, internet‑tooling apps, and full agents with memory—and argues only defense‑in‑depth holds up in practice paper page.

- Highest‑severity issues: prompt injection, jailbreaks, model/system tampering, insider misuse, and common‑stack vulns paper page.
- Prescribes layered controls: input/output filters, retrieval hardening, least‑privilege tools, sandboxed code, continuous monitoring.
- Introduces a compact scenario string to record design choices and compare setups, plus a STRIDE analysis across the four archetypes.
Practitioners steer English retrieval toward GTE‑ModernColBERT/ColBERT‑small; Reason‑ModernColBERT noted
Retrieval engineers recommend ModernColBERT variants for English tasks—GTE‑ModernColBERT or ColBERT‑small—with Reason‑ModernColBERT as a “fun” option, and tease a forthcoming comparison resource model tips, open source note.
- ColBERT’s late‑interaction pattern remains a strong default for semantic search; community momentum around open implementations is growing open source note.
- Expect updated, side‑by‑side resources to simplify model selection trade‑offs (quality vs. latency vs. footprint) model tips.
🎥 Creative gen: dynamic CFG, RL for diffusion and tool‑orchestrated visuals
A research‑heavy day for image/video generation quality control and multimodal tool orchestration; fewer consumer feature launches.
Dynamic CFG learns per‑prompt guidance; Imagen 3 hits up to 55.5% human‑preference wins
Instead of a fixed classifier‑free guidance (CFG) scale, a new method adapts CFG step‑by‑step using online feedback signals (CLIP alignment, fidelity, and a preference reward), producing a unique schedule for each prompt with ~1% overhead method summary, paper link.
- Results on Imagen 3 show up to a 55.5% human preference win‑rate on text‑rendering prompts and strong overall alignment/quality gains ArXiv paper.
- The framework is solver‑agnostic and generalizes beyond small models to production‑scale systems, with no base‑model changes required method summary.
DiffusionNFT: forward‑process RL boosts SD3.5‑M GenEval from 0.24 to 0.98 in 1k steps
NVIDIA’s DiffusionNFT fine‑tunes diffusion models directly on the forward process via contrastive positives/negatives, delivering policy improvement without CFG or trajectory storage and training with arbitrary black‑box solvers method teaser, paper link.
- On SD3.5‑Medium, GenEval jumps 0.24→0.98 in 1k steps, exceeding FlowGRPO’s 0.95 which needed >5k steps and CFG ArXiv paper.
- The approach reports ~25× efficiency vs FlowGRPO and integrates multiple reward models; project details and code accompany the paper project page.
LLM‑Interleaved routes tools for factual visuals; hits 100% tool accuracy on internal set
LLM‑I treats report generation as planning: the model writes text, tags where and what images to add, then a parser runs the right tool—web search for real photos, diffusion for creative images, code for charts, and image editing—before reinserting results paper brief, thread recap, ArXiv paper.

- Reinforcement learning mixes rule checks (format and image counts), a language judge, and a multimodal judge; the visual score only counts if rules pass, pushing compliance first paper brief.
- The pipeline samples multiple end‑to‑end candidates, filters broken tool calls, retries code for charts, improves search/diffusion picks, and selects the best final output paper brief.
SPATIALGEN turns 2D layouts into complete 3D indoor scenes
A layout‑guided 3D scene generator produces full indoor environments from high‑level room layouts, targeting controllable, coherent scene synthesis for design and simulation workflows paper link, author discussion, Hugging Face paper.
- The work emphasizes layout conditioning to maintain global structure while populating objects realistically; the authors opened a discussion thread for technical Q&A author discussion.
💼 Enterprise moves and paywalls for heavy features
Light but notable go‑to‑market updates: regional rollouts and pricing signals for compute‑heavy features. Excludes infra CAPEX (separate).
OpenAI to launch compute‑intensive features behind Pro and add‑on fees
OpenAI signaled a new pricing tier for heavy features: initial access will be limited to Pro subscribers with additional per‑feature fees, with a stated goal of driving costs down over time Altman post.

- First wave will test appetite for high‑compute tools while maintaining broad access later as costs fall Altman post.
- Expect near‑term monetization experiments as the company explores “what’s possible with significant compute power at current costs” Altman post.
Notion launches AI Agents with Business‑tier gating or separate add‑on
Notion rolled out assignable AI Agents, available on Business or higher plans, or purchasable as a separate subscription Notion announcement.
- Pricing and packaging indicate sustained paywalling for agentic, compute‑heavier workflows Notion announcement.
- Enterprise‑friendly positioning (task assignment, role fit) aligns with cross‑team automation use cases.
Perplexity opens Comet browser to Pro users in India
Perplexity expanded its Comet AI browser to all Perplexity Pro subscribers in India, its second country after the U.S. Comet India. This extends early access to the company’s premium, AI‑forward browsing experience.

- CEO note confirms broader availability for Pro, hinting at phased regional rollouts Comet India.
- Expansion suggests continued paywalled gating for the most compute‑heavy in‑browser features.
Cohere opens Paris office as EMEA hub
Cohere established a Paris office as its EMEA headquarters, naming leadership for regional operations and public policy Cohere EMEA, Cohere blog.
- Signals deeper enterprise go‑to‑market in Europe and adjacent regions Cohere EMEA.
- Expect tighter engagement with EU enterprise and government buyers as model governance and compliance needs rise Cohere blog.
Microsoft pilots Copilot “Career Coach” with live portrait avatars
Microsoft is testing a Copilot Labs “Career Coach” that simulates interviews using live Portrait avatars, tailored to your CV and job description Career Coach leak, TestingCatalog post.

- Early access suggests a staged rollout and potential premium gating within Copilot tiers Career Coach leak.
- Targets a concrete enterprise pain point (interview prep and upskilling) in HR/L&D settings TestingCatalog post.
🗣️ Voice agents, TTS/STT updates
A quieter day: a Grok web ‘Imagine with speech’ sighting and indie STT deals; fewer lab‑scale voice launches.
Grok ‘Imagine with speech’ shows up on the web with a Speech toggle
A UI sighting shows Grok’s Imagine tool offering a Speech mode on the web, with quick presets like Custom, Spicy, Fun, and Normal, following up on Read aloud (Grok added voice read‑outs). The sidebar also lists Search, Ask, Voice, and Imagine, hinting at broader browser integration. See the interface in UI screenshot.
- The screenshot suggests speech‑enabled image generation directly in browser, not just mobile clients UI screenshot.
- If rolling out, this would unify search, voice, and image features in one web surface for xAI.
Indie Mac speech‑to‑text goes viral with a $19 lifetime offer
A creator‑made Mac STT app is pushing a one‑time $19 lifetime price, drawing rapid interest and early buyers who plan head‑to‑heads with Wispr and Monologue lifetime offer, offer link, buyer note.
- Early adopters report purchasing to support the indie developer and will share comparisons with popular STT tools buyer note.
- The pay‑once model undercuts typical subscription pricing for always‑on dictation lifetime offer.
🤖 Embodied platforms and world‑model planning
A couple of embodied signals: desktop open robot release and humanoid competition note; planning/world‑model papers are in Research.
Reachy Mini refresh: 28 cm desktop robot ships with 15+ behaviors, Python SDK and sim toolkit
Pollen Robotics’ Reachy Mini returns as a compact, community‑friendly desktop robot with a near‑360° view, plug‑and‑play behaviors, and a Python SDK plus simulator to prototype before hardware arrives Feature brief.
- Two versions: Lite (tethered, compute‑less) and full unit (Raspberry Pi 5, Wi‑Fi, battery) Feature brief
- Form factor: ~28 cm tall, 16 cm wide, ~1.5 kg; motorized head with 6 DoF, full‑body rotation, expressive antennas Feature brief
- Sensors and I/O: Wide‑angle camera, 5W speaker, 2–4 mics; full model adds accelerometer Feature brief
- Software: 15+ ready‑to‑run behaviors, Python SDK, and a behavior hub for sharing and pulling community behaviors Feature brief
Protoclone musculoskeletal android touts 1,000 ‘myofiber’ muscles and active cooling, pitched as Figure competition
A musculoskeletal biped dubbed Protoclone is being framed as a credible Figure competitor, with claims of 1,000 myofiber muscles on a human‑like skeleton and a chassis that “sweats” to shed heat Android overview.
- Architecture: Muscle‑like actuation mapped onto a human‑analog skeleton for lifelike motion envelopes Android overview
- Thermal design: Frame‑level cooling (“sweating”) to sustain continuous operation under load Android overview
- Market signal: Community commentary positions it alongside Figure as humanoid competition to watch Android overview
🧩 Chips and neuromorphic directions
Not a big chip‑news day; we note neuromorphic‑leaning model claims and AMD‑aligned kernel work lives under Systems. This is scoped narrowly today.
SpikingBrain touts 85–98% energy cuts with spiking + linear attention LLMs
A new SpikingBrain technical report outlines spiking‑inspired LLMs with linear/hybrid attention that claim 85.2–97.7% lower energy than FP16/INT8 baselines on neuromorphic hardware, while holding competitive accuracy on standard benchmarks paper thread, ArXiv paper.

- Models: SpikingBrain‑7B (linear) and SpikingBrain‑76B‑A12B MoE (hybrid‑linear), trained on ~150B/160B tokens paper thread.
- Reported quality: 7B posts MMLU 65.8 and CMMLU 71.6; 76B‑A12B reaches MMLU 73.6 and CMMLU 78.9 (table screenshots) paper thread.
- Long‑context behavior: 1B demo shows near‑constant decode throughput as output length rises to 256K, vs steep slowdowns for Llama‑3.2‑1B (plot) paper thread.
- Efficiency pitch: event‑driven spiking, linear/hybrid attention, and sparsity target constant/linear complexity for training and inference, with stability reported on large non‑NVIDIA clusters paper thread.