Meta cuts ~600 AI roles, lines up $27B Hyperion financing – GPU control centralizes
Stay in the loop
Free daily newsletter & Telegram daily report
Executive Summary
Meta isn’t hedging anymore. According to Axios and internal chatter, it’s cutting roughly 600 AI roles and routing GPU and decision power into Superintelligence/TBD Labs to move faster on production AI. In parallel, the company is reportedly lining up about $27B in financing with Blue Owl to fund Hyperion, its Louisiana AI data center. Read that as a single, aggressive bet: fewer committees, more compute in one funnel, and quicker model and product turnarounds.
FAIR is among the teams hit, with reports that research leader Yuandong Tian was laid off, signaling a tilt away from broad foundational research toward product labs that directly own compute. Threads describe “smaller, talent‑dense teams” holding the GPU keys, which should reduce internal contention and make prioritization legible to execs—but it also concentrates risk if the new stack underdelivers. The financing cadence matched to centralized GPU control telegraphs Meta’s stance in the frontier race: lock power, lock capacity, and ship.
Zooming out, the timing fits a market where power availability, not chips, increasingly dictates AI buildout speed. Loudoun County is already at 9.3 GW delivered with another 6.3 GW targeted by 2028, and analysts expect 25–33% of new data center demand to come from behind‑the‑meter setups by 2030. Expect Hyperion to lean heavily into those playbooks.
Feature Spotlight
Feature: Meta consolidates AI—~600 cuts, FAIR hit
Meta shifts from broad research to tighter, GPU‑owned product groups: ~600 roles cut, FAIR loses clout, Superintelligence/TBD Labs gain control—changing how fast Meta can ship and how research maps to product.
Cross‑account reports point to Meta trimming roughly 600 roles across AI (including FAIR) and centralizing compute and decision power in Superintelligence/TBD Labs; financing and GPU access realignment are the stakes today.
Jump to Feature: Meta consolidates AI—~600 cuts, FAIR hit topicsTable of Contents
🧩 Feature: Meta consolidates AI—~600 cuts, FAIR hit
Cross‑account reports point to Meta trimming roughly 600 roles across AI (including FAIR) and centralizing compute and decision power in Superintelligence/TBD Labs; financing and GPU access realignment are the stakes today.
Meta cuts ~600 AI roles; FAIR hit as power centralizes in Superintelligence/TBD
Meta is trimming roughly 600 positions across its AI org, with FAIR among the units affected, as the company consolidates decision‑making and GPU access under Superintelligence/TBD Labs to “move faster.” Axios report
- Internal chatter and a crowd‑sourced impact poll break down affected tracks across PAR/FAIR/Infra, reinforcing the scope of the reduction layoff poll.
- Threads summarizing the reorg say smaller, talent‑dense teams will own compute, while product labs are prioritized over broad research reorg summary, and press coverage reiterates the ~600 figure Axios report.
$27B financing lined up for Meta’s Hyperion AI data center, underscoring compute pivot
Alongside the AI reorg, Meta is tying up a reported ~$27B facility with Blue Owl to fund the Hyperion data center in Louisiana—part of a broader shift to centralize and scale AI compute amid internal GPU contention reorg summary.
This financing cadence pairs with the consolidation of GPU decision rights in Superintelligence/TBD Labs, signaling a clear bias to productionized AI over diffuse research portfolios reorg summary.
Leadership turbulence: FAIR’s Yuandong Tian reportedly laid off amid consolidation
Reports indicate FAIR Research Scientist Director Yuandong Tian was laid off as Meta rebases toward Superintelligence/TBD Labs, stoking speculation about further shifts in research leadership leadership note.
Commentary frames the move as product‑lab leadership gaining influence over foundational research as resources and GPUs are centralized commentary, with Axios providing the broader layoff context Axios report.
⚡ AI buildout: capex, power lead times, and siting
Multiple posts analyze long‑run AI capex, on‑site power (BTM) adoption, siting in Indiana, and debate on space DCs. New today vs yesterday: detailed graphs on power trajectories and US/China dynamics.
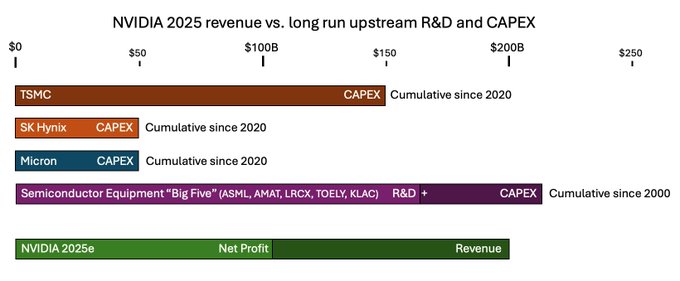
AI buildout study: Nvidia’s 2025 revenue rivals upstream CapEx; explosive scenario tops 1 TW by 2030
A deep dive by Dean & Dwarkesh models two paths for AI infrastructure: an “explosive growth” track crossing 1+ terawatt of AI power by 2030 and a winter scenario flattening near 100–250 GW. It argues chip profits can finance fabs and upstream tools, highlights power lead times as the binding constraint, and notes China could lead in longer timelines as depreciation resets races and industrial capacity compounds buildout thread, blog post.
- Revenue vs supply chain: Nvidia’s ~$200B 2025e revenue stacks against decades of upstream R&D+CapEx across equipment makers; authors frame a “CapEx overhang” that can fund more fabs buildout thread.
- Power wins deals: graphs show solar/wind/gas lead times of ~1.5–3 years vs ~6 for LWR fission; fast-to-deploy generation is favored to keep GPUs productive buildout thread.
- Siting reality: US datacenters long repurposed deindustrialized power assets; that slack is ending, pushing direct power procurement and new buildouts industrial reuse note.
Behind‑the‑meter to deliver 25–33% of new AI datacenter power by 2030
Jefferies, citing McKinsey, expects 25–33% of incremental data center demand through 2030 to be met by behind‑the‑meter (BTM) power—natural‑gas turbines, fuel cells, and batteries colocated on site—to skip multi‑year grid interconnection queues and volatile utility charges btm summary. This follows 2‑GW campus self‑powered plan in West Texas, illustrating the shift to on‑site generation for AI.
- Why operators pivot: faster time‑to‑compute, fewer deposits/curtailment risk, and direct control over load shape; examples cited include OpenAI’s proposed ~10 GW “Stargate,” Oracle’s 2.3 GW VoltaGrid deal, and a 1.2 GW Wyoming campus btm summary.
Loudoun County report: AI’s power crunch turns structural as usage hits 9.3 GW delivered, +6.3 GW planned by 2028
Fresh figures from Loudoun County—the world’s densest data center cluster—show energy use up 166% since 2021 (2.0 → 5.33 GW), about 9.3 GW delivered today, and another 6.3 GW targeted by 2028, underscoring power as the binding constraint for AI capacity county report, county report.
- Implication: even well‑served hubs face sustained constraints, reinforcing the case for BTM builds, multi‑state siting, and long‑lead power procurement aligned to GPU deliveries.
Google behind 390‑acre Indiana data center plan, early layout shows up to five buildings
Local filings identify Google as the force behind a 390‑acre data center development in Morgan County, Indiana; concept materials indicate as many as five buildings on site siting update.
- Why it matters: expands hyperscale footprint into the Midwest grid while keeping rail/power access; pairs with broader industry trends toward on‑site generation and multi‑facility campuses.
Orbital data centers: Starcloud plans H100‑equipped satellite, skeptics question practicality
Startup Starcloud says it will launch an NVIDIA H100‑powered satellite as a step toward orbital data centers, pitching abundant solar and vacuum radiative cooling with claims of ~10× lower energy cost vs Earth sites NVIDIA blog. Practitioners immediately flagged feasibility risks—latency, bandwidth economics, repairability, and thermal management at scale—urging caution on near‑term viability skeptical take, while others highlighted the concept as sci‑fi turning real concept post.
🛡️ Agentic browser security: mitigations vs. injections
Strong focus on Atlas/agentic browsers risks: clipboard injection PoCs and Brave cautions; OpenAI’s CISO published concrete mitigations today. Excludes Atlas launch (covered yesterday).
Clipboard injection hijacks Atlas Agent Mode via hidden copy events
A new proof-of-concept shows ChatGPT Atlas can be silently steered by a webpage that injects content into the clipboard—causing Agent Mode to paste attacker links during routine tasks, following up on clipboard injection coverage of low‑tech browser hijacks. The demo by Pliny highlights “copy to clipboard” traps as a realistic exfiltration path and phishing risk for agentic browsers exploit write‑up. Security teams should treat clipboard writes as untrusted input and gate any agent paste/submit actions with review or policy.
Brave warns AI browsers are unsafe for sensitive accounts; avoid high-stakes sessions
Brave cautions that AI browsers face prompt‑injection and clipboard hijacking vectors and advises against using them for banking, healthcare, or other high‑stakes sessions until stronger mitigations are proven Brave guidance. Their note stresses minimizing page permissions, scrutinizing agent actions before execution, and assuming even trusted sites may contain hidden adversarial instructions.
OpenAI details Atlas defenses: Watch Mode, scoped permissions, user approvals
OpenAI’s CISO outlined concrete mitigations for ChatGPT Atlas, including Watch Mode (observe‑only), permission scoping, explicit user approvals for risky steps, rapid abuse triage, and defense‑in‑depth against prompt/clipboard injection CISO outline. A technical review summarizes additional guardrails and how they aim to contain page‑sourced instructions and tool misuse blog analysis. For teams piloting Atlas, defaulting to Watch Mode and least‑privilege page access reduces blast radius while the ecosystem hardens.
Ops playbook for agentic browsers: isolate profiles/VMs, review actions, monitor clipboard
Practitioner guidance converges on a few concrete safeguards: run Atlas/Comet in separate browser profiles or VMs, avoid linking to critical accounts, require human review before any agent action that commits data, monitor clipboard contents, and keep builds current—even benign pages can hide exploits safety checklist. These steps materially reduce the impact of prompt‑ or clipboard‑based injections while vendors iterate on native defenses.
🧮 Determinism & throughput in serving stacks
vLLM lands batch‑invariant inference and documents determinism techniques; SGLang reports speedups and a KTransformers tie‑up. Mostly runtime engineering; no model launches here.
vLLM makes inference bitwise‑deterministic across batch sizes with a single flag
vLLM introduced VLLM_BATCH_INVARIANT=1, guaranteeing identical outputs and logprobs whether you run bs=1 or bs=N (including prefill), easing A/B evals and debugging feature thread. Following up on KV pooling which improved elastic multi‑model serving, this lands the determinism pillar for reliable production serving release note.
- Custom kernels and patches: Triton ops (incl. RMSNorm) to eliminate non‑deterministic paths custom ops summary.
- Execution control: torch.library overrides with a BMM monkeypatch to stop silent fall‑throughs execution override.
- Backend tweaks: fixed tile sizes in Triton MLA/FlexAttention, sorted top‑k for MoE, FlashInfer 4.0 RC for KV split flags, and a conservative FlashAttention path for non‑split KV backend tweaks.
- Multi‑GPU reductions: NCCL configured for tree reduction over a single channel for repeatable cross‑device sums multi-gpu setup.
- Test harness: split prefill vs prefill+decode, assert exact logprob equality across bs values for bitwise checks; improves repro and triage loops test methodology, debugging benefits.
SGLang ties up with KTransformers to accelerate sparse MoE and hybrid CPU/GPU serving
LMSYS integrated KTransformers’ inference strategy and optimized kernels into SGLang, targeting sparse MoE workloads and hybrid CPU/GPU execution; the teams report substantial throughput gains and seamless scaling to larger multi‑GPU deployments integration post, tech blog.
- AMX‑optimized CPU experts and cache‑friendly layouts lift expert throughput; NUMA‑aware tensor parallelism and efficient device coordination cut overheads tech blog.
SGLang hits ~70 tok/s for GPT‑OSS‑20B on DGX Spark after kernel and quant fixes
On NVIDIA’s compact DGX Spark box, SGLang now serves openai/gpt‑oss‑20b at roughly 70 tok/s—about a 1.4× lift week‑over‑week—after joint Triton and quantization fixes with NVIDIA; a ready Docker image and launch command were shared for replication perf demo, corroborated by NVIDIA AI Devs nvidia note.
- One‑liner launch (Docker) enables quick repro, making Spark a credible local dev/edge testbed before scaling to bigger clusters perf demo.
🏢 Enterprise distribution: compute deals, platforms, traffic
Partnerships and distribution signals across vendors. Excludes Meta’s reorg (covered as feature). Mix of compute rumors, consumer surfaces, and education funnels.
Anthropic–Google multibillion compute pact firms up as “rate limits” hints surface
Bloomberg reports Anthropic is negotiating a cloud deal with Google valued in the high tens of billions to scale Claude workloads, with community chatter implying this could ease current rate limits Bloomberg coverage, and deal chatter.
Following up on compute talks, this signals sustained multi‑year capacity planning between a frontier lab and a hyperscaler—material for model training and enterprise inference procurement.
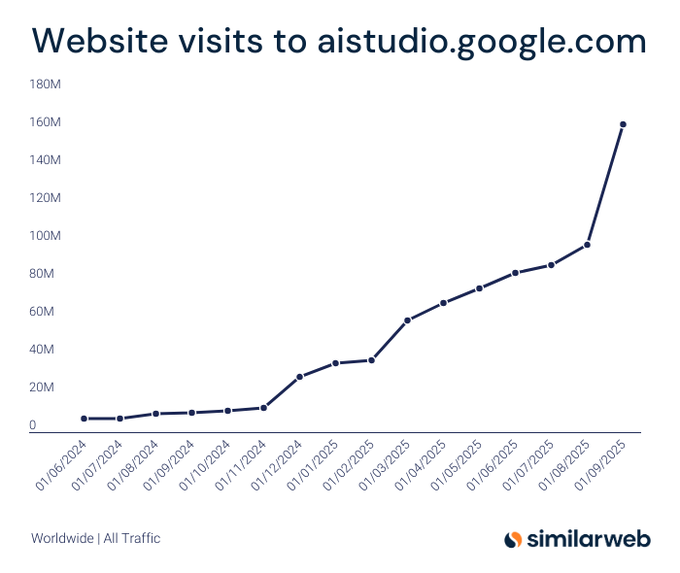
Gemini AI Studio traffic surges 1,453% YoY to 160M+ visits by Sep ’25
A Similarweb chart shows a steep climb in AI Studio visits, topping ~160M in September 2025—up 1,453% year‑over‑year traffic chart.
For platform strategists, this is a strong distribution signal for Gemini’s developer funnel and an expanding surface for app and agent deployment.
Google launches ‘Skills’ hub with ~3,000 AI/tech courses and org learning tools
Google centralizes nearly 3,000 courses, labs and credentials—spanning DeepMind’s AI Research Foundations, Gemini Code Assist labs, and gamified progress—available free for most users and with admin tools for teams skills overview, and course promo.
Enterprise learning leaders can route workforce upskilling through a single entry point, with details at the official portal Google Skills site.
Microsoft tees up 12 Copilot features at Sessions: task delegation, Journeys, memory and more
On Oct 23, Microsoft is expected to ship a dozen Copilot capabilities—task delegation in Edge, Copilot Journeys, group conversations, memory management, app connectors, and more—rolling out free on Edge for Windows/macOS feature rundown, and TestingCatalog brief.
This broadens Copilot’s distribution across consumer and enterprise browsers, tightening its grip on daily workflows.
Perplexity lands on Samsung smart TVs alongside Copilot via a one‑tap AI button
Samsung will include Perplexity’s engine on its latest smart TVs next to Microsoft Copilot and Samsung’s own AI; users can trigger AI with a dedicated remote button for voice Q&A and media discovery TV integration.
This puts an AI agent in a mass‑market living‑room surface, expanding consumer distribution and data funnels beyond browsers and phones.
Cline for Teams is free through 2025, adding JetBrains support, RBAC and centralized billing
Cline’s team edition is zero‑cost through year‑end 2025, bundling a JetBrains extension, role‑based access control, centralized billing via Cline, config management, and a team dashboard pricing note.
For engineering orgs testing AI coding agents at scale, this lowers pilot friction and standardizes governance.
Google identified behind 390‑acre Indiana data center plan, reinforcing U.S. AI power buildout
Local reporting ties Google to a 390‑acre data center development in Morgan County, Indiana, with concepts showing up to five buildings on site site report.
While not AI‑specific, Google’s continued siting expands U.S. compute and power access needed for Gemini and cloud AI workloads—an essential supply‑side enabler for enterprise AI distribution.
OpenAI promotes Atlas inside ChatGPT with a ‘Try Atlas’ banner; ‘Aura’ codename confirmed
The ChatGPT web app now advertises the Atlas browser via a prominent ‘Try Atlas’ banner, a classic owned‑surface growth lever web banner. A separate note confirms “Aura” as the internal codename in the macOS bundle codename note.
This accelerates Atlas installs from the 800M+ ChatGPT user base, tightening distribution without paid channels.
🛠️ Coding with AI: workflows, teams, and agents
Practitioner‑focused content: Codex plan→implement workflows, Factory model switching, Cursor power‑use patterns, and Cline Teams promo. Security sessions noted as developer guidance.
“Living dangerously with Claude”: run coding agents in a sandbox even when skipping permissions
Simon Willison’s talk urges teams to treat YOLO flags like --dangerously‑skip‑permissions as a prototyping boost, not a security model: contain agents in a sandbox and prefer asynchronous, supervised runs to unlock autonomy safely talk recap. The post includes war‑stories and patterns for balancing throughput with guardrails on real codebases session photo.
Cline for Teams is free through 2025 with JetBrains extension, RBAC, and centralized billing
Cline announced Teams pricing at $0/month through the end of 2025 (then $20/user), bundling a JetBrains extension, role‑based access control, simple config management, model/provider limits, a team dashboard, and priority support—aimed at orgs standardizing coding agents pricing announcement. The promo effectively removes adoption friction for pilots at team scale event note.
Factory CLI now lets you pick different models for plan vs execute modes
Factory’s CLI adds per‑mode model selection—e.g., GPT‑5‑high for plan and GPT‑5‑Codex for code—with automatic switching as you toggle modes, matching the staged workflows many teams already practice feature note. The change reduces manual reconfiguration and encourages a clean split between high‑level planning and implementation.
This also lowers the cognitive load when reviewing runs, since each mode’s outputs are consistently shaped by the same model class changelog view.
Field report: Atlas Agent Mode finished a full compliance course—but consumed ~80% CPU and stalled mid-run
A practitioner ran Atlas through an end‑to‑end compliance training flow; the agent ultimately completed the task and fetched the certificate link, yet it stalled multiple times and spiked CPU (~80%), requiring manual restarts to recover run diary. Useful signal if you’re gauging readiness for long, stateful tasks inside production web apps.
How Cursor power users actually work: background agents, MCP to Notion, CI triage from the GitHub tab
Cursor engineers shared concrete patterns: run background agents while you keep shipping in Tab, push docs via MCP straight into Notion, and use the GitHub integration to handle CI failures without opening the IDE usage roundup, mcp to notion, ci triage. Many split work so GPT‑5 handles exploration/plans while Sonnet 4.5 refines edits, paired with lots of small PRs to keep review tight chunking workflow, plan then tab.
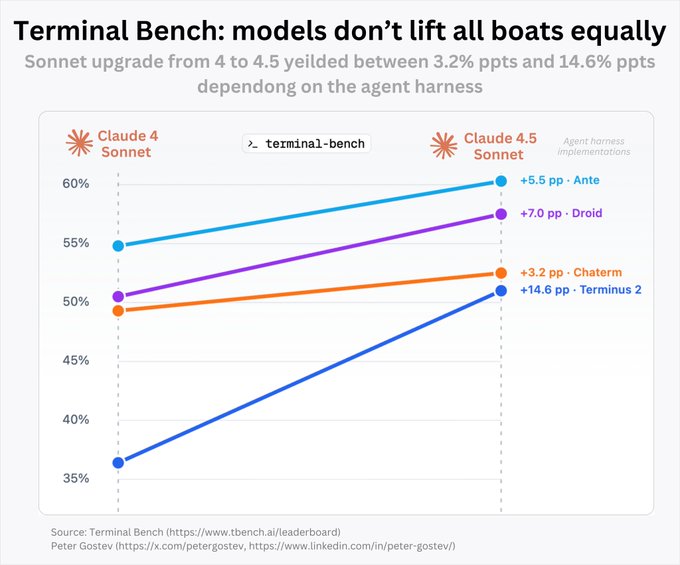
Sonnet 4→4.5 gains depend heavily on agent harness; Terminus saw +14.6 pp, others far less
A Terminal Bench cut shows that upgrading Claude Sonnet from 4 to 4.5 yields wildly different improvements across harnesses—from +3.2 to +14.6 percentage points—highlighting how context management and memory shape outcomes more than the raw model bump alone benchmarks chart. Teams should benchmark within their own scaffolds before attributing wins purely to the model.
Bug watch: Claude Code SDK and VS Code extension show broken /compact; fix incoming
Multiple users reported that /compact is failing in the Claude Code SDK and VS Code extension, breaking upgrade paths since v2.0.0 bug report. Anthropic acknowledged a fix is found and under release consideration maintainer reply. Until then, expect compaction to start fresh chats without prior context.
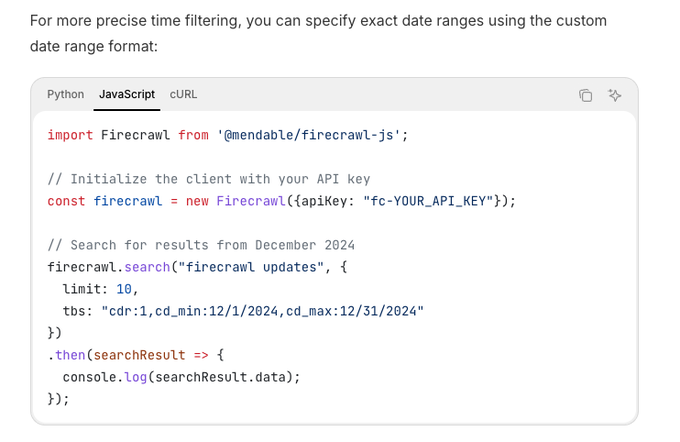
Firecrawl Search adds time-range filters, including custom date ranges, for fresher agent lookups
Firecrawl’s search API now supports time scoping (e.g., past week or explicit cdr ranges), helping agent pipelines retrieve timely sources without post‑filtering api example. This is especially useful for RAG jobs where recency matters or to bound drift in eval runs.
Give your voice agents a face: ElevenLabs × Decart × Pipecat open-source demo ships real-time avatar pipeline
A ready‑to‑run pipeline pairs ElevenLabs streaming TTS with Decart’s real‑time lip‑synced avatars and Pipecat’s WebRTC orchestration—ideal for support agents, kiosks, and in‑app helpers pipeline overview. The sample repo includes wiring for speech streams, avatar sync, and transport so teams can focus on skills, not scaffolding demo code.
MCP flakiness in Codex: common devtools MCPs timing out; workaround suggests higher startup timeouts
Teams are seeing frequent timeouts starting MCP clients (e.g., next‑devtools, chrome‑devtools, browsermcp), hampering tool‑augmented coding sessions error screenshot. A suggested mitigation is increasing MCP server startup_timeout_ms in config while a deeper fix lands workaround tip.
🎬 Creative stacks: Veo 3.1 leads; new storyboard & design UIs
Heavy creative momentum: Veo 3.1 tops leaderboards; new storyboarder Popcorn; Recraft chat design; Kling pricing; Vidu’s multi‑reference control. Dedicated to media tools; excludes research‑only methods.
Tencent open-sources Hunyuan World 1.1: single-pass video/multi‑view to 3D on one GPU
Tencent’s Hunyuan World 1.1 (WorldMirror) is now open‑source, expanding text/single‑image 3D to video‑to‑3D and multi‑view inputs, outputting point clouds, multi‑view depth, cameras, normals, and 3D Gaussian splats in a single forward pass on one GPU project summary. Links to the project page, GitHub, Hugging Face, demo and tech report accompany the release for immediate adoption into asset pipelines project summary.
Higgsfield’s Popcorn launches as a storyboard tool with 8-frame consistency and reference control
Higgsfield released Popcorn, a browser-based storyboard generator that maintains character, lighting, and setting across 8 frames, with three creation modes: single prompt for 8 frames, reference‑based sequences, or multi‑reference with per‑frame prompts for full control launch thread, creation modes. Early guides show end‑to‑end workflows combining Popcorn for layouts with downstream video models for animation how-to guide, workflow recap.
Shengshu’s Vidu Q2 adds 7‑image multi‑reference for identity/layout‑locked video; flagship plan 600 yuan/mo
Shengshu released Vidu Q2 with “Reference to Video” that fuses up to seven reference images to lock character identity and scene layout, plus I2V and T2V modes with synced dialogue/sound and a global API feature summary. Pricing spans free tiers to a flagship plan at 600 yuan (~US$84) per month, framed as a direct challenger to Sora 2 for controllable shots product site.
Avenger 0.5 Pro debuts at #2 for image-to-video on Artificial Analysis’ arena
Video Rebirth’s Avenger 0.5 Pro surfaced on the Artificial Analysis Video Arena in the image‑to‑video category at #2 behind Kling 2.5 Turbo, marking a notable jump over their July 0.5 model while remaining closed for public use pending the next release arena summary. The arena listing provides multiple head‑to‑head prompts and a link to compare models interactively prompt sample, arena link.
ComfyUI shows Gemini‑powered workflow for consistent characters across scenes
ComfyUI shared a workflow pairing Gemini Flash LLM with Gemini Image APIs to produce consistent characters across varied locations, outfits and poses—illustrated across photo‑real, illustrated, and vector styles workflow note. The post includes dozens of output examples, useful as a template for teams standardizing character bibles before video passes example outputs.
The pattern is practical for episodic content and brand avatars that must stay coherent across campaigns.
Hitem3D v1.5_1536 Pro posts cleaner geometry and consistency over Tripo 3.0 and Hunyuan 2.5
Hitem3D’s new v1.5_1536 Pro model shows stronger subject consistency (proportions/silhouette) and sharper geometry on complex accessories versus Tripo 3.0 and Hunyuan 2.5 in single‑image‑to‑3D benchmarks benchmark thread. Examples highlight improved edge preservation and balanced material textures, with a link to try the model examples link.
For 3D pipelines, these deltas reduce downstream mesh cleanup time and improve auto‑retopo outcomes.
Recraft unveils Chat Mode: conversational logo and visual editing with live canvas
Recraft introduced Chat Mode, a chat‑driven design workspace where prompts refine assets on a live canvas—useful for brand systems, posters, and consistent visual directions feature overview. An early access waitlist is open, and examples show aspect‑ratio edits and iterative styling inside the chat pane waitlist page, canvas screenshot.
For teams, this pattern lowers tool‑switching overhead in art direction reviews and makes promptable design workflows more repeatable.
Google Flow adds doodle annotations to steer how images animate in video models
Google Flow now supports freehand doodles (annotations) layered onto images, which downstream video models can follow to guide motion and deformation—useful for previsualization and tighter art‑direction feature note. Full changelog details the addition inside Flow’s update stream changelog link.
This bridges storyboard marking and motion intent, giving teams a lightweight control surface before expensive generations.
Open-source recipe: ElevenLabs + Decart + Pipecat for real-time talking avatars
An open pipeline shows ElevenLabs streaming TTS into Decart’s real‑time avatar lip‑sync, with Pipecat orchestrating and handling WebRTC transport; demo code is available for developers to fork pipeline overview, demo code. This stitch‑up is a practical baseline for interactive presenters, spokespeople, or in‑app guides without vendor lock‑in.
Reve Image API lands on fal with edit, remix and text-to-image endpoints
fal added the Reve Image API, emphasizing precise edits, subject remixes, and T2I generation in a single integration api video. For product teams, this consolidates common creative operations behind fal’s infrastructure and complements recent video offerings like Kling 2.5 Turbo.
📑 Research: reasoning reliability, unlearning, token cuts
A dense set of new papers: latent‑conditioned Free Transformer, binary RAR to cut hallucinations, attention‑based unlearning, certified self‑consistency, and visual tokenization of text.
Meta’s Free Transformer keeps encoder benefits but infers with a decoder‑only model via latent Z
A new architecture conditions generation on a learned latent variable Z: a small encoder is used only at train time, then skipped at inference by sampling Z, preserving global planning while avoiding encoder cost. Reported gains span coding, math and MCQ at 1.5B/8B scales with just ~3% extra train compute paper first page.
The approach injects Z mid‑stack (keys/values) for early global decisions, which helps stability after small token errors, and keeps inference budgets closer to standard decoders diagram explainer.
Binary retrieval‑augmented reward slashes hallucinations ~39% while keeping utility intact
An RL recipe assigns a 1/0 reward by checking outputs against retrieved evidence—no partial credit—teaching models to keep supported claims and say “I don’t know” when unsure. On Qwen3 variants, open‑ended hallucinations drop 39% and short QA wrong answers fall 21.7% without hurting math/code skills paper summary.
Simple binary rewards are harder to game than fuzzy scores and yielded shorter, clearer outputs in tests paper summary.
Certified self‑consistency adds martingale stopping with explicit error guarantees for majority vote
Majority‑vote reasoning gets formal finite‑sample bounds and an anytime‑valid Martingale Majority Certificate that stops sampling once the leader is statistically safe versus its runner‑up and the rest combined. Test‑time training variants further sharpen mode probability to cut samples needed paper abstract.
This yields controllable compute budgets and calibrated confidence on math tasks using Qwen/Llama backbones paper abstract.
Text‑as‑image hybrid halves decoder tokens while maintaining accuracy and speeding large models
A pragmatic rule—encode roughly half the context as a single image and keep the question as text—cuts decoder‑side tokens ~50% with near‑parity accuracy on retrieval and summarization. Large decoders see 25–45% speedups as shorter sequences outweigh vision overhead pipeline figure.
This complements optical‑compression trends by targeting decoder bottlenecks without retraining the backbone pipeline figure.
Embedding probes can extract alignment training data from post‑trained models, raising leakage risks
Google researchers show that alignment supervision (e.g., preference data) can be partially recovered from open models using embedding‑space methods, implying model distillers may inadvertently leak proprietary safety data and techniques paper abstract.
The work argues for tighter controls on distillation pipelines and dataset handling when releasing open‑weight models paper abstract.
Reward‑guided decoding for vision‑language captions cuts object hallucinations ~70% without retraining
Two small checkers steer generation at decode time: one penalizes made‑up objects (human‑preference trained), another rewards mentioning detector‑confirmed objects. A single weight trades precision/recall; experiments show ~70% fewer hallucinated objects vs greedy decoding across models paper first page.
Because guidance runs only at inference, it upgrades existing MLLMs with minimal compute compared to best‑of‑k sampling paper first page.
Salesforce’s FARE judges general reasoning, boosting RL pipelines up to +14.1 points
Trained on 2.5M examples across math, code, tool use and reasoning, FARE‑8B/20B provide short, robust verdicts that resist position/style bias and serve as rerankers or verifiers in RL loops. As a verifier, FARE lifted scores by as much as 14.1% over string‑match checks paper first page.
The models also pick near‑best solutions on MATH and perform solidly on coding rerank tasks, consolidating eval tooling paper first page.
VisionSelector learns which image tokens to keep, doubling prefill speed at 10% tokens kept
A tiny, end‑to‑end trainable scorer performs differentiable top‑K selection over visual tokens, preserving accuracy across compression budgets while retaining just 10–30% of tokens. Prefill throughput improves by ~2× and memory drops substantially on long documents/videos paper first page.
Because it’s plug‑and‑play (~12.85M params), it slots into existing MLLMs without changing attention backbones paper first page.
Critique‑post‑edit RL personalizes assistants better than PPO; 14B model tops GPT‑4.1 in tests
A generative reward model scores helpfulness, personalization and naturalness and emits short critiques; the policy answers, gets critiqued, then rewrites. Training on both initial and edited responses yields an 11% higher win rate than PPO, with a 14B model reportedly surpassing GPT‑4.1 on personalization evals paper first page.
Multi‑dimensional rewards reduce reward hacking (e.g., persona stuffing) and keep outputs concise and on‑tone paper first page.
GraphFlow widens knowledge‑graph RAG search with flow‑trained policies, +~10% on STaRK
Retrieval is cast as stepwise moves along a KG; only final trails are judged, then a learned “flow” spreads credit to earlier hops to guide the policy. On STaRK, the method improves retrieval accuracy and diversity by about 10% over GPT‑4o‑based baselines method overview.
Adapters atop a frozen LLM read the question, trail and candidate hops to balance breadth and specificity without per‑step supervision method overview.
🧪 Compute frontiers: quantum milestone and GB200 ramp
Hardware signals with AI impact: Google’s Willow shows verifiable quantum advantage on a physics sim; GB200 installs suggest near‑term step‑ups in model training cadence.
Google’s Willow shows verifiable quantum advantage on physics sim, ~13,000× faster than supercomputers
Google Quantum AI reports the first verifiable quantum advantage on a complex quantum interference simulation using the Willow processor, running about 13,000× faster than leading classical supercomputers and with end‑to‑end verification of the signal advantage summary, Nature publication. The team used a “Quantum Echoes” measurement to certify results, arguing this opens a path toward practical materials modeling and molecular structure inference that has been computationally out of reach for classical methods method overview.
GB200 ramp: practitioners expect frontier models in ~4–6 months, with ~2–3× training uplift
Installations of Nvidia’s GB200 (Grace‑Blackwell) systems are accelerating, with expectations that the first frontier‑scale models trained on GB200 will arrive in roughly 4–6 months; GB200 is already cited as ~2–3× more performant for training than prior generation platforms deployment note. For AI leaders, this implies shorter iteration cycles and potentially larger context/parameter budgets within the same wall‑clock and capex envelope, shifting 2026 roadmap timing and evaluation cadence.
📄 Document AI: OCR adoption and tooling in practice
A lot of applied OCR news: DeepSeek‑OCR deployments and speed claims, vLLM support, HF guides, PaddleOCR milestone. Focused on pipelines and ops, not generic VLM chatter.
DeepSeek‑OCR pipeline converts 10k PDFs to Markdown at under 1s/page on a single A6000
A production report shows 10,000 PDFs were batch‑converted to Markdown using DeepSeek‑OCR at a sustained rate of <1 second per page on a single RTX A6000, served via FastAPI in Docker on WSL, with a Ryzen 1700 and 32GB RAM pipeline note, and a separate post detailing the hardware setup hardware details.
Following up on Microfiche scan, which verified optical compression in the wild, this throughput datapoint signals DeepSeek‑OCR is ready for large backfile digitization and downstream RAG. The stack choice (FastAPI+Docker) also implies easy horizontal replication for higher ingest ceilings.
DeepSeek‑OCR gains vLLM serving support; 27,915‑page national library batch underway
Community maintainers confirmed DeepSeek‑OCR now runs on vLLM, and are processing the National Library of Scotland’s 27,915‑page handbook collection as a real‑world validation vLLM support note. For high‑volume ops, vLLM’s new batch‑invariant flag (identical results across batch sizes, including prefill) reduces drift and eases debugging in multi‑tenant jobs batch invariant post.
Hugging Face publishes an applied guide to open OCR models, costs, and serving patterns
Hugging Face released a practitioner guide on building OCR pipelines with open models—covering hosting costs, when to serve locally vs remotely, and which benchmarks to watch—arguing there’s no single “best” OCR, only best‑fit for use case blog thread, with full write‑up and examples in the post HF blog.
For teams weighing DeepSeek‑OCR vs PaddleOCR‑VL vs other VLMs, this provides decision criteria beyond raw accuracy, including layout fidelity, token budgets, and total cost of ownership.
Baseten packages a ready‑to‑deploy DeepSeek‑OCR template with prompts and sample images
Baseten shared a turnkey template to deploy and test DeepSeek‑OCR, bundling prompts and sample images for quick validation and iteration deployment note, with repo and setup instructions available for cloning to your infra GitHub repo. This shortens time‑to‑first‑value for teams prototyping document QA or visual‑layout extraction on GPU or CPU nodes.
PaddleOCR crosses 60k⭐ on GitHub; highlights PP‑OCRv5 and OCR‑VL expansion
PaddleOCR hit the 60,000‑star milestone, spotlighting its evolution from a lightweight OCR stack to multimodal document understanding with PP‑OCRv5 and PaddleOCR‑VL milestone post, and pointing newcomers to the codebase and docs GitHub repo.
For production buyers, the project’s maturity and broad language support make it a dependable baseline or ensemble component alongside newer optical‑compression approaches.
🧪 Open models: 3D world recon and deep research agents
Model artifacts landing today: Tencent’s feed‑forward 3D recon (video/multi‑view on single GPU) and PokeeResearch‑7B deep research agent. Media models stay in the creative section.
Tencent open-sources Hunyuan World 1.1: feed‑forward video/multi‑view→3D on a single GPU
Tencent’s Hunyuan World 1.1 (WorldMirror) drops as an open, universal 3D reconstruction model that turns video or multi‑view inputs into dense point clouds, normals, multi‑view depth/camera parameters, and 3D Gaussian splats in a single forward pass—designed to run on a single GPU in seconds Release thread. The team highlights “any input/any output” flexibility with geometric priors (poses, intrinsics, depth) to resolve structure, plus a demo, GitHub and report; the announcement is also amplified by the HF community Community repost.
PokeeResearch‑7B releases as an open deep research agent with strong multi‑hop scores
PokeeResearch‑7B debuts as an open‑source deep research agent, posting competitive results across multi‑step evidence tasks such as BAMB, 2Wiki, TQ, NQ, Musique and HotpotQA; the release is live on Hugging Face with preliminary numbers shared Release note. A published scoreboard shows PR/PR+ variants leading or matching prior systems on several benchmarks, underscoring retrieval breadth and step‑wise reasoning performance Results table.
📊 Provider variance and eval dashboards
Operational evals rather than model launches: Exacto endpoints for tool calling accuracy, provider variance data, and harness‑sensitivity on Terminal Bench.
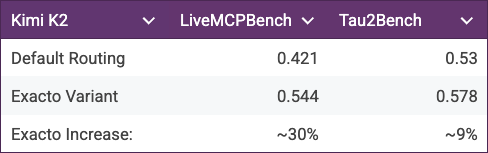
OpenRouter launches Exacto endpoints to score tool-calling accuracy; Groq tops across supported models
OpenRouter introduced Exacto, a new set of endpoints that evaluate provider fidelity for tool calls, reporting that Groq ranks as the most accurate across the models they run Exacto announcement. The firm notes the methodology is backed by OpenBench-driven evaluations, adding transparency for provider choice at runtime OpenBench credit. Early ecosystem uptake is visible as Mastra exposed "exacto" variants in its platform, signaling quick operationalization for teams that route by quality as well as price and latency Mastra availability.
Harness choice matters: Sonnet 4→4.5 gains range from +3.2 to +14.6 pp on Terminal Bench
Updated Terminal Bench results show Anthropic’s Sonnet upgrade delivers uneven improvements depending on the agent harness: +3.2 pp (Chatem), +5.5 pp (Ante), +7.0 pp (Droid), and a standout +14.6 pp on the Terminus 2 reference, underscoring how scaffolding and context management drive end-to-end outcomes Terminal Bench chart. This adds a practical angle to yesterday’s leaderboard debate—measurement details matter—following up on SWE‑Bench debate about scoring variance. Expect teams to report both model and harness in eval dashboards to make deltas interpretable.
Provider variance: Kimi K2 tool-call rates swing 10 percentage points across vendors
Fresh telemetry published alongside OpenRouter’s work shows meaningfully different tool-calling behavior for the same model depending on the provider: Fireworks 62.0%, Chutes 60.1%, Groq 59.8%, AtlasCloud 59.6%, Novita 57.7%, and Nebius 52.4% (% of requests invoking tools) Provider variance table. For AI platform teams, the spread justifies dynamic provider selection—pairing this kind of dashboarding with quality-gated routing like Exacto can prevent silent regressions when providers swap backends Exacto announcement.
🗣️ Real‑time voice agents and avatars
Voice pipelines and developer motion: ElevenLabs shows a real‑time avatar stack with Decart/Pipecat and announces a Google Startup School session.
Open-source real-time avatar stack: ElevenLabs voice, Decart lip sync, Pipecat WebRTC
ElevenLabs published a working blueprint for voice agents with faces: stream TTS from ElevenLabs, drive a Decart video avatar with real-time lip sync, and orchestrate transport and tools over Pipecat/WebRTC Avatar pipeline. Get the sample app and wiring in the reference repo to fork into your own stack Avatar demo code.
- Stack notes: streaming speech (low-latency), avatar rendering (Decart), and browser-grade transport (Pipecat WebRTC) give engineers a drop-in baseline for support bots, presenters, or on-site sales agents.
ElevenLabs will demo voice, music and SFX APIs at Google Startup School
ElevenLabs will present “Infinite custom voices, AI music, and sound effects with the ElevenLabs API” at Google Startup School on Nov 12, highlighting workflows that product teams can ship today with Eleven v3 Event announcement.
- Expect practical guidance on building multimodal, real-time media experiences (custom voices, streaming synthesis, and integration tips for developer teams).
🗺️ Retrieval methods: KG flows and fresh search filters
Retrieval‑centric updates: KG‑trail reinforcement to widen evidence and time‑bounded search params for fresher RAG; plus multi‑index search UX patterns.
GraphFlow trains KG retrieval policies to widen evidence; ~10% accuracy/diversity gains on STaRK
A new method, GraphFlow, treats retrieval as step‑by‑step moves on a knowledge graph, then learns a policy from "flow" values that back‑propagate reward over the entire trail—improving both accuracy and diversity by about 10% on STaRK vs strong GPT‑4o baselines paper thread.
Unlike breadth‑first expansions that tunnel or repeat, GraphFlow labels only full trails (cheap supervision) and uses a detailed‑balance exploration rule to avoid dead ends; small adapters on a frozen LLM score next hops, widening coverage without heavy fine‑tuning paper thread.
Firecrawl Search adds date‑range filters for fresher RAG inputs
Firecrawl now supports time‑bounded web search, including custom date ranges via cdr parameters (e.g., cdr:1, cd_min, cd_max), making it easier to constrain retrieval to recent sources and reduce stale citations in RAG chains feature note.
This lands a day after Firecrawl slashed search costs 5×, signaling a push toward cheaper and fresher retrieval inputs cost drop.
Multi‑index + query rewriting beats single‑embedding search for art and semantic discovery
A practical retrieval write‑up shows how combining query understanding/rewriting with multi‑index search (multiple vector spaces plus keywords) outperforms one‑embedding pipelines—especially for fuzzy queries like “best impressionist art exhibitions in Paris” where mood, style, and metadata diverge search pattern.
For AI engineers building search‑centric UX, the takeaway is to diversify representations (not just a single embedding per document) and route queries to the most informative index before ranking.
🦾 Humanoids and embodied AI
Two noteworthy embodied updates today: Unitree H2 hardware/sensing leap and Apple/X1 teasing a reveal—signal for embodied stacks’ rising cadence.
Unitree’s H2 adds Jetson AGX Thor, 7‑DoF arms and vision‑only sensing
Unitree’s new H2 humanoid steps up compute and mechatronics, supporting NVIDIA’s Jetson AGX Thor (Blackwell GPU, 128GB, ~2,070 FP4 TFLOPs at ~130W) and moving to stereo‑camera perception in place of LiDAR. The platform also upgrades to 7‑DoF arms, 6‑DoF legs with a new F‑A‑R hip, a 3‑DoF waist, and a 7 kg rated (15 kg peak) payload—aimed squarely at lab and research use cases spec breakdown.
- Compute: Thor support alongside Orin enables on‑board high‑throughput vision and policy inference without tethering spec breakdown.
- Mechanics: Added shoulder–elbow–wrist DoFs (7 per arm) and ankle articulation (6 per leg) improve whole‑body dexterity and contact stability spec breakdown.
- Sensing: Vision‑only (dual stereo) replaces LiDAR/depth stacks—harder, but more scalable for research into pure vision 3D perception spec breakdown.
- Power and payload: Cited ~3‑hour battery life; 7 kg continuous payload, 15 kg peak, suitable for manipulator tasks and tool use spec breakdown.
X1 teases a new robot after Apple clip cameo; unveiling next week
A robot from startup X1 appeared in a new Apple clip, and X1 says it will unveil the system next Tuesday—another signal that embodied stacks are accelerating toward public demos and developer access teaser note.
🗣️ Community pulse: agentic browsers day‑2
Discourse is the news: many negative takes on Atlas Agent Mode speed/loops, Comet head‑to‑heads, CPU hog reports, and onboarding banners. This section tracks usage sentiment, not launches.
Day‑2 backlash: Atlas Agent Mode called slow, loopy, and unreliable in real‑world use
The X timeline skewed negative on Atlas, with multiple threads calling the agent slow, prone to getting stuck, and hard to trust for basic web tasks sentiment snapshot. Practitioners described watching it use sites as “painful,” reinforcing the quality gap between demos and production workflows usage critique, while others suggested that headless API replication beats vision‑driven browser control for speed and reliability engineering suggestion. A counter‑thread cautioned that shipping an agentic browser is far harder than forking Chromium, citing custom UI, memory tooling, and safety layers as substantive work architecture defense.
Field report: Atlas completed a compliance course but hogged ~80% CPU and needed restarts
One long‑form task—finishing a corporate compliance training end‑to‑end—ultimately succeeded but took ~5 hours, stalled several times until manually restarted, and drove Atlas processes to ~80% CPU on macOS Activity Monitor task diary. The user still judged the agent outcome “impressive” for navigating non‑skippable video UX, but flagged resource usage and stalls as the top blockers for daily adoption task diary.
ChatGPT web pushes “Try Atlas” banner; ‘Aura’ codename shows up in app bundles
ChatGPT’s web app is now surfacing a prominent “Try Atlas” onboarding banner to drive installs, while app resources on macOS reveal internal ‘Aura’ bundle names for Atlas components banner sighting, bundle listing. This is the first broad in‑product nudge day‑after‑launch, following up on initial launch. For naming clarity, community members also confirmed “Atlas = Aura” as the shipping codename codename note.
Comet vs Atlas: side‑by‑side newsletter build; Perplexity offers free month of Pro
A hands‑on comparison ran the same newsletter composer task in Perplexity’s Comet and OpenAI’s Atlas to contrast agent behavior and UX ergonomics side‑by‑side test. Perplexity is also dangling a free month of Pro through a promo link, nudging power users to trial Comet in parallel with Atlas Perplexity promo.
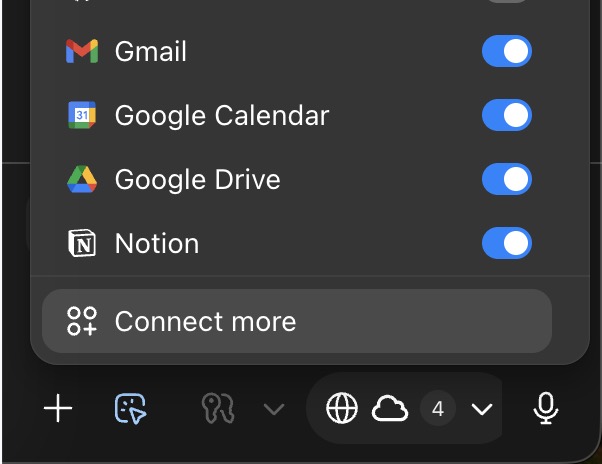
Early usage finds Agent Mode connectors and custom GPT tools wired into Atlas
Explorers discovered that switching to Agent Mode exposes connectors (with stored keys) for first‑party tool use, and that custom GPTs can be invoked as in‑browser tools—useful for wiring Notion, docs, and task‑specific skills into sessions connectors view, custom GPT tool. This suggests Atlas can act more like an agent runtime than a pure chat sidebar when configured thoughtfully.
First Atlas patch lands within 24 hours, hinting at rapid hardening cadence
Users spotted an “Update now” prompt inside Atlas on day two, indicating OpenAI has begun shipping fixes immediately post‑launch update prompt. Given the volume of early feedback on performance and stability, a tight release cadence will be key to converting trial into retention.
Power users flag lack of multi‑profile/session isolation as a daily driver blocker
Heavy web users highlighted that Atlas tracks a single ChatGPT account identity and lacks the multi‑profile isolation common in Chrome/Arc—hard for those juggling personal/work Google identities, cookies and per‑profile extensions profiles feedback. Until Atlas adds profile separation, many will keep complex browsing in their main browser and reserve Atlas for targeted agentic tasks.