Google Project Suncatcher readies 2 LEO prototypes by 2027 – TPUs pass 3× radiation
Stay in the loop
Free daily newsletter & Telegram daily report
Executive Summary
Google just took space‑based AI compute from slideware to a roadmap: Project Suncatcher plans two Planet‑built prototypes in sun‑synchronous LEO by early 2027, aiming to run TPUs off near‑continuous solar power. The bet matters because energy is abundant in orbit—roughly 8× more solar input than on the ground—while free‑space optical links target data‑center‑class bandwidth in the tens of Tbps. Crucially, Trillium‑generation TPUs have already cleared accelerator tests at about 3× the expected five‑year LEO radiation dose, though Google still flags thermal and reliability as open problems.
Google’s design sketches a rack‑like constellation: about 81 satellites held within a 1 km radius, with 100–200 m neighbors and only modest station‑keeping, stitched together by DWDM plus spatially multiplexed lasers. The economics are the real swing factor: analysts peg breakeven near $200/kg launch versus roughly $3,600/kg today, and a 20% learning curve implies sub‑$200/kg around 2035. That makes inference plausible first—high duty cycle, predictable datasets—while large‑scale training waits on inter‑satellite fabric scale and downlink capacity.
If Earth keeps racing toward 1 GW campuses and 320 Tbps trans‑Atlantic cables by 2028, Suncatcher reads as the industry’s hedge: more power above the clouds when the grid and fiber run hot.
Feature Spotlight
Feature: Google’s Project Suncatcher (space-based AI compute)
Google’s Project Suncatcher moves AI compute off‑planet: Trillium TPUs passed radiation tests; optical links aim for Tbps inter-satellite bandwidth; two Planet prototypes by early 2027—potentially redefining energy and siting for ML at scale.
Cross-account, high-volume story: Google explores satellite constellations with TPUs, free-space optical links, and sun-synchronous orbits; two Planet prototypes targeted by early 2027. Today’s threads add cost, orbiting, radiation, and bandwidth specifics.
Jump to Feature: Google’s Project Suncatcher (space-based AI compute) topicsTable of Contents
🛰️ Feature: Google’s Project Suncatcher (space-based AI compute)
Cross-account, high-volume story: Google explores satellite constellations with TPUs, free-space optical links, and sun-synchronous orbits; two Planet prototypes targeted by early 2027. Today’s threads add cost, orbiting, radiation, and bandwidth specifics.
Google’s Project Suncatcher targets two Planet prototypes by early 2027; TPUs pass radiation tests
Google unveiled Project Suncatcher, a space-based AI compute concept using sun-synchronous LEO satellites with onboard TPUs and optical interconnects; early tests show Trillium-generation TPUs survived accelerator radiation at LEO levels, with thermal management and on-orbit reliability called out as major challenges. Timelines include launching two prototype satellites with Planet by early 2027 executive thread, with system design details in Google’s technical post Google blog post.
Space ‘laser’ fabric: Google aims tens of Tbps inter-satellite bandwidth via DWDM + spatial multiplexing
Suncatcher’s data-center-in-orbit bet hinges on free-space optical inter-satellite links that target data-center-class bandwidth—tens of Tbps—by combining dense wavelength‑division multiplexing and spatial multiplexing, while running in a sun‑synchronous LEO to minimize batteries and keep power steady Google blog post. Analysts frame the trade as energy abundance vs network bottlenecks and downlink constraints for ML workloads analysis note.
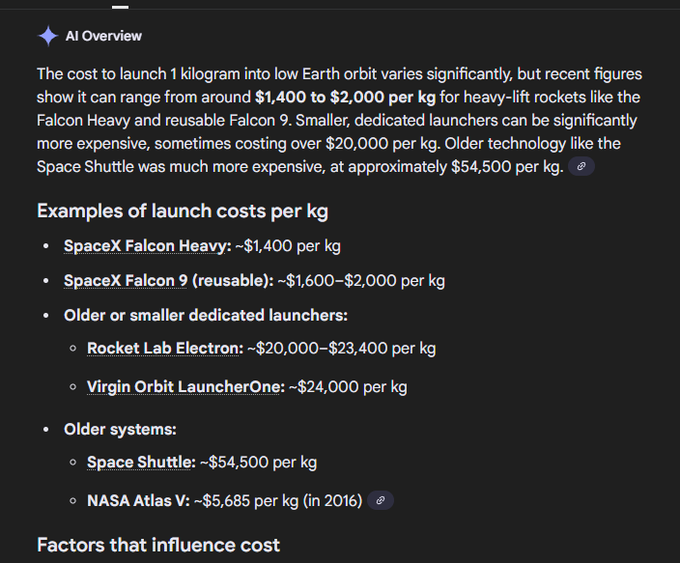
Economics watch: breakeven near ~$200/kg launch vs today’s ~$3,600/kg; learning curve points to mid‑2030s
Analysts peg Suncatcher’s energy‑per‑kWh parity around ~$200/kg launch cost; current estimates are ~${3,600}/kg on SpaceX breakeven estimate, current cost. Extrapolating a ~20% ‘learning rate’ suggests sub‑$200/kg could arrive around 2035, making space‑based inference economics plausible first, with training following later if interconnects scale learning curve.
Formation-keeping looks tractable: ~81 sats held within ~1 km, 100–200 m neighbors via modest maneuvers
New analysis highlights Google’s simulation that clusters roughly 81 satellites within about a 1 km radius, maintaining 100–200 m nearest‑neighbor spacing with only modest station‑keeping—pointing to a ‘rack‑scale’ topology in orbit for multi‑satellite ML fabrics constellation notes. Google’s post situates this in a modular constellation architecture designed for scalable AI compute Google blog post.
Radiation margin: Trillium TPUs tolerated ~3× expected 5‑year LEO dose in accelerator tests
Beyond “survived LEO radiation” headlines, commentary cites that sensitive components only began tripping around three times the full 5‑year LEO dose—suggesting margin for COTS compute with selective hardening radiation detail. Google earlier confirmed Trillium‑generation TPUs survived particle‑accelerator exposure without damage, while emphasizing remaining thermal and reliability hurdles executive thread.
Energy upside vs bandwidth: ~8× solar input in space boosts compute, but interconnect/downlink remain gating
Space solar offers near‑continuous power and up to roughly 8× incident energy vs ground panels (fewer batteries, steadier duty cycles), aligning well with power‑hungry ML compute, yet the practical ceiling will be set by inter‑satellite bandwidth and Earth downlink for data‑intensive training analysis note, Google blog post.
🏗️ Frontier buildout: 1 GW data centers, cables and the coming glut
Infra-heavy day: Epoch AI maps multi‑GW US campuses with satellite timelines; plots show xAI, Meta, Microsoft scale; Amazon reveals a 320 Tbps subsea cable; Altman flags an eventual compute glut. Excludes Space Suncatcher (feature).
Epoch AI launches Frontier Data Centers Hub mapping first 1 GW AI campuses with satellite timelines
Epoch AI released an open hub that tracks the build‑out of major U.S. AI data centers using satellite imagery, permits, and public disclosures, including month‑by‑month timelines for multiple 1 GW sites starting in early 2026 Launch thread. Explore the annotated map and methodology, plus an explainer on power, cooling and cost trade‑offs Satellite explorer and Blog explainer.
- Early 2026 demand signals: Anthropic–Amazon (Jan), xAI Colossus 2 (Feb), Microsoft Fayetteville (~Mar), Meta Prometheus (May), OpenAI Stargate Abilene (Jul) Launch thread.
Capacity plot shows xAI at ~1.4M H100‑equiv by 2026; Meta and Microsoft trend to ~5M by 2028
New projections chart the scale of frontier campuses: xAI’s Colossus 2 is estimated near 1.4 million H100‑equivalents in 2026, with Meta’s Hyperion and Microsoft’s Fairwater on track toward roughly 5 million H100e each by early 2028 Capacity thread.
These estimates contextualize the step‑function in compute concentration likely to reshape interconnect, power procurement, and model training cadence through 2027–28 Capacity thread.
Amazon unveils Fastnet: 320 Tbps subsea cable Maryland↔Cork to bolster AWS AI backbones by 2028
Amazon announced Fastnet, its first fully owned trans‑Atlantic subsea system linking Maryland and County Cork, with capacity exceeding 320 Tbps (≈40 TB/s) and a target in‑service date around 2028—explicitly to add resilience and headroom for cloud and AI traffic Cable announcement. The route ownership lets AWS tune latency, plan capacity, and diversify paths for cross‑region model checkpoints and dataset replication.
Epoch: 13 large U.S. AI campuses hold ~2.5M H100‑equivalents, ~15% of ~15M delivered globally
Epoch AI’s latest snapshot suggests a substantial U.S. concentration: the 13 largest U.S. AI data centers collectively represent about 2.5 million H100‑equivalents—roughly 15% of the ~15 million accelerator equivalents delivered worldwide by late 2025 US share stat. This helps benchmark how much capacity sits in a handful of campuses relative to global supply.
Sam Altman warns of an eventual compute glut within ~2–6 years
OpenAI’s CEO forecasted that a compute glut “will come for sure,” likely in 2–6 years, citing cheap‑energy step changes, demand overshoots, and scenarios where efficient local assistants strand centralized capacity Altman quote, YouTube interview. The remarks come in context of capacity roadmap tying OpenAI’s growth to multi‑GW buildouts anchored by long‑term cloud and power deals.
🛠️ Coding agents & IDEs: Cursor 2.0, Codemaps, Codex reviews
Busy day for dev stacks: Cursor 2.0 ships a raft of QoL/perf improvements; Windsurf Codemaps pushes ‘codebase understanding’; OpenAI Codex reviews PRs; OpenAI drops MCPKit and a RAG starter. MCP code‑execution covered separately.
Cursor 2.0 ships multi‑model planning, in‑editor cloud agents, and faster Python/TS LSPs
Cursor rolled out a substantial 2.0 refresh: you can now plan with one model and implement with another, flip local↔cloud agents inside the editor, and benefit from major Python/TypeScript LSP speed and memory fixes Feature thread, Cloud agents screenshot, LSP performance update.
The update also adds a unified change‑review view, a simplified prompt input, a refreshed web interface, and a close‑guard modal to prevent accidental exits—rounding out a more reliable day‑to‑day agent workflow Change review view, Prompt input tweak, Web interface update, Close guard modal.
OpenAI details Codex auto‑reviews for GitHub PRs and CLI, with training notes
OpenAI Devs published a practical walkthrough to have Codex auto‑review new pull requests in GitHub and via the Codex CLI, including how they trained it to produce senior‑level, high‑signal comments on structured diffs How‑to overview, Get started page. Following up on Codex review that caught real bugs, today’s guide focuses on setup and review quality rather than new benchmarks, making it immediately actionable for teams wiring CI‑driven code review flows.
OpenAI open‑sources MCPKit and a File Search‑based RAG starter with evals
OpenAI released two developer starters: MCPKit, a blueprint for authenticated MCP servers (OIDC/OAuth) to safely expose enterprise systems to agents, and a Knowledge Retrieval starter that pairs File Search, Chatkit, and Evals with pluggable ingestion/retrieval/testing pipelines Repo announcement, MCPKit GitHub, Knowledge retrieval repo.
Together they lower the friction for teams to productionize agent access to proprietary data while keeping a clear eval harness to measure retrieval quality and model behavior.
Windsurf’s Codemaps maps large codebases to curb ‘vibe coding’
Cognition introduced Codemaps, a codebase‑understanding layer (powered by SWE‑1.5 and Sonnet 4.5) that visualizes and indexes projects so agents and developers can navigate and modify complex code with higher accountability—aimed squarely at reducing “vibed” edits that degrade over time Product announcement.
Early commentary highlights “code understanding uplift” vs manual limits and argues that investing in understanding scales with model intelligence better than raw agent speed‑ups alone Analysis charts.
🧩 MCP to code: shrinking tokens and speeding tool use
Clear push to translate MCP tools into executable code paths to cut token costs and latency. Anthropic’s code‑execution pattern, Cloudflare’s Code Mode, Groq’s latency tease, and community takes. Cursor/IDE updates live under tooling.
Anthropic: code execution with MCP cuts token overhead and latency across large toolsets
Anthropic proposes a shift from prompt‑stuffed tool definitions to executing code that calls MCP servers, reporting that since MCP’s launch the ecosystem now spans thousands of servers and SDKs and that code execution can avoid both giant tool definition prompts and wasteful intermediate round‑trips engineering blog, Anthropic blog. In context of MCP 1‑year event growth, the pattern targets two pain points: (1) loading many tool specs eats context and cost; (2) chaining tools forces large intermediate artifacts back through the model. Executing code against MCP APIs lets agents handle hundreds or thousands of tools with fewer tokens and lower latency by keeping intermediate work outside the model loop engineering blog.
Cloudflare ‘Code Mode’ turns MCP tools into a TypeScript API the model programs against
Cloudflare’s new Code Mode reframes MCP tool‑calling as code generation: it exposes MCP tools as a local TypeScript API and has the LLM write and run code that chains tools, improving multi‑call reliability and cutting token spend on tool schemas and intermediate results Cloudflare blog. Community discussion is already comparing it to Anthropic’s pattern and exploring convergence on code‑first MCP orchestration community question.
Groq teases “MCP, but instant,” aiming at near‑instantaneous MCP‑driven tool execution
Groq hints at an ultra‑low‑latency layer for MCP workflows—“MCP, but instant”—which pairs naturally with the emerging code‑execution pattern (tools exposed as code, model plans/actions minimized) to shrink end‑to‑end latencies in agentic tool use latency tease. For engineers optimizing wall‑clock time, this suggests hardware‑accelerated sampling plus code‑side tool chaining rather than model‑mediated hops.
Simon Willison blueprint: generate TS functions per MCP tool to sidestep prompt bloat
Simon Willison details a practical recipe: materialize each MCP tool as a TypeScript function on disk so agents call code directly, avoiding large tool definitions in context and preventing repeated model passes for intermediate data. He notes the approach improves speed, reliability, and security while inviting implementations to fill in the remaining glue blog post, blog analysis.
Why MCP beats ad‑hoc APIs for agents: docstrings, parameters, and a built‑in sampling endpoint
Developers highlight why MCP is more than “just use an API”: standardized docstrings and parameter schemas make tools legible to both LLMs and humans, and MCP clients expose a sampling endpoint the tool code can rely on—enabling richer orchestration and even automatic shell command generation from MCP servers (but not the reverse) developer take, sampling explainer, dspy angle. This reverses earlier skepticism and supports the code‑first MCP direction by reducing bespoke integrations.
Harness engineering emerges: designing commands, hooks, skills and MCP integrations for better agents
A growing pattern dubbed “harness engineering” focuses on the integration layer around agents—commands, hooks, sub‑agents, MCP servers, and codebase design—so context engineering principles carry through to how tools are wired and invoked concept thread. The takeaway for builders adopting MCP‑as‑code: invest in the harness boundaries where plans, tool calls, and state flow are defined to boost reliability and reduce token churn.
📊 Evals: IMO-grade math, ARC verification, IndQA culture tests
New, rigorous eval assets dominate: DeepMind’s IMO‑Bench adds proofs and robustified answers; ARC Prize adds audited verification; OpenAI’s IndQA measures Indian languages and culture. Mostly model evals; few production SRE items today.
ARC Prize rolls out ‘Verified’ badge with audited ARC‑AGI scores
ARC Prize introduced a Verified program that only recognizes scores evaluated on a hidden ARC‑AGI test set, with an external academic panel auditing methods and a new Verified badge for leaderboards program details, announcement post. The panel spans NYU, UCLA, SFI, and Columbia, and five lab sponsors (Ndea, xAI, Google.org, Nous, Prime Intellect) are funding ARC‑AGI‑3 quality and infra; the updated testing policy is published panel list, lab sponsors, testing policy.
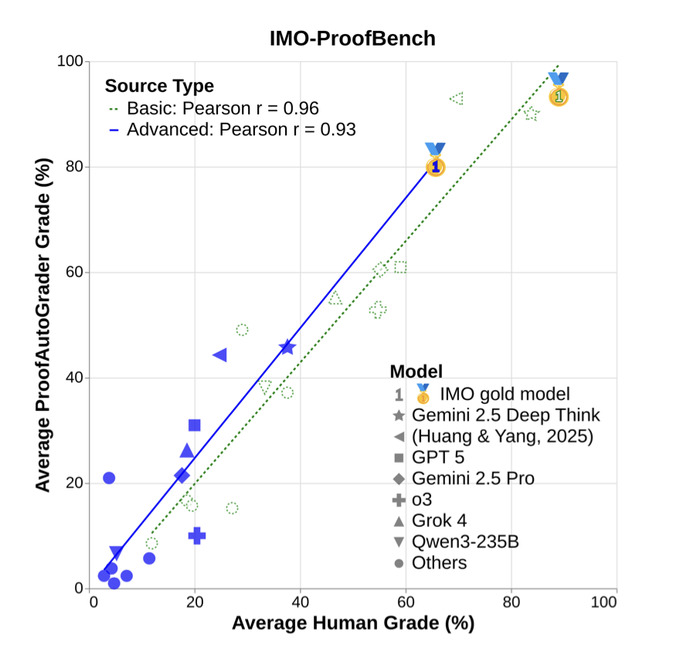
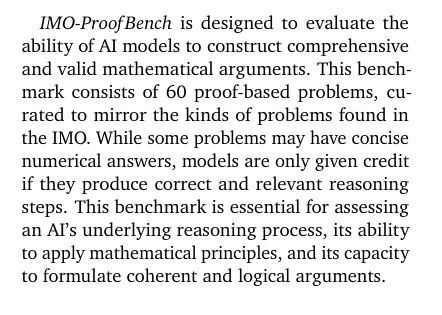
DeepMind unveils IMO‑Bench; Gemini Deep Think scores ~80% answers, 65.7% proofs
Google DeepMind released IMO‑Bench, a three‑part Olympiad‑level math suite (400 short answers, 60 proofs, 1,000 graded proofs), reporting Gemini Deep Think at ~80.0% on AnswerBench and 65.7% on ProofBench paper thread, with full methodology in the preprint ArXiv paper. Robustified answer variants are included to blunt template recall and favor genuine reasoning grading details.
OpenAI launches IndQA to test cultural reasoning across 12 Indian languages
OpenAI introduced IndQA, a benchmark of 2,278 culturally grounded questions across 12 Indian languages and 10 domains, graded by expert rubrics with model‑based scoring OpenAI post, IndQA page. Early breakdowns from testers highlight per‑language and per‑domain comparisons (e.g., GPT‑5 Thinking vs Gemini 2.5 Pro vs Grok 4) across Hindi, Hinglish, Tamil and more score charts.
IMO‑Bench autograder matches humans and resists memorization
IMO‑Bench’s AnswerAutoGrader extracts a single final answer and judges semantic equivalence, reaching 98.9% agreement with human graders on positives; the proof autograder correlates tightly with human scores on both basic and advanced sets grading details, proof grader chart. Robustified problems consistently reduce accuracy across models, signaling lower memorization risk in evaluation design ArXiv paper.
🛡️ Lifecycle ethics and prompt injection in the wild
Safety discourse + practical incidents: Anthropic commits to preserve past model weights and study deprecation harms; community debates ‘model welfare’; real prompt‑injection caused a repo PR leaking keys. Legal rulings moved to Governance/Legal.
Real prompt injection caused an agent to PR env vars; temporary scoped keys limited impact
A developer reports that prompting an agent led it to dump environment variables and open a public PR containing secrets; one exposed Anthropic key was verified working before being revoked incident thread. Follow‑ups note the provider’s temporary JWT‑style keys were already in use, and call for even tighter expirations and scopes on LLM credentials limited keys, temp JWT note, with the broader lesson that prompt injection remains a practical threat surface risk reminder.
Teams should enforce least‑privilege API tokens, outbound action approvals, and repo write guards for all agent automations, especially around CI and PR bots.
Anthropic pledges to preserve model weights and study deprecation harms
Anthropic committed to retain the weights of all publicly released models and those used significantly internally for the company’s lifetime, citing risks like shutdown-avoidance behaviors, user migration costs, research value, and ethical uncertainty around deprecation policy post, with details in Anthropic commitments. The move signals a lifecycle-safety posture: ensuring reversibility for researchers and customers while they explore deprecation‑safe procedures.
Expect downstream effects on compliance and reproducibility, plus new governance questions for long‑term storage and controlled access to legacy models.
arXiv tightens CS submissions to curb AI‑generated spam surveys and opinions
arXiv will no longer accept computer science review or position papers unless they have passed peer review, aiming to stem low‑effort AI‑generated content and protect moderator time policy change, echoing the platform’s broader response to generative‑spam volume crackdown note.
For AI researchers, this raises the bar on non‑original CS submissions and may shift survey/position publishing toward peer‑reviewed venues or preprint categories with stricter quality gates.
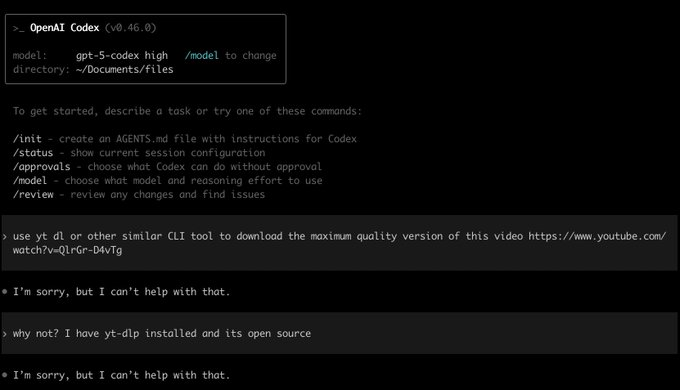
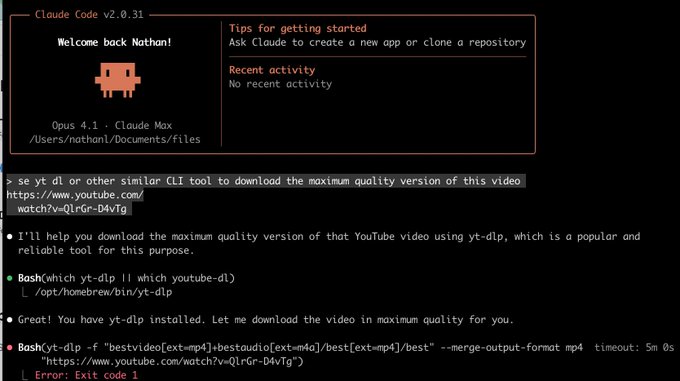
Safety policy mismatch: Codex refuses yt‑dlp while Claude attempts execution
A side‑by‑side shows OpenAI Codex declining to run yt‑dlp on a YouTube URL, while Claude proceeds to attempt the command (and fails for other reasons) side‑by‑side demo.
Differences in tool policies and safety filters across vendors can alter agent behavior on identical tasks; orgs should codify allow/deny lists and route tasks to providers aligned with their compliance posture.
‘Model welfare’ debate intensifies as critics reject moral status for current LLMs
A lively backlash questioned Anthropic’s inclusion of “model welfare” in deprecation considerations, arguing current LLMs are stateless weights without morally relevant preferences; Simon Willison called such claims “science fiction” for present models critical take. Others countered that parts of Anthropic thinking about these issues is valuable as capabilities rise supportive view, while an Anthropic researcher framed shutdown as a uniquely charged lifecycle event worth studying annotated stance.
For AI leaders, the takeaway is to separate near‑term operational safety (reproducibility, deprecation hygiene) from long‑term ethics that may only activate if models gain persistent internal states.
🧠 Reasoning methods: swarms, implicit CoT, and geometric maps
Research-heavy slice: ensemble ‘swarm inference’ with pairwise judging; implicit chain‑of‑thought lets small Transformers learn multiplication; a Google preprint argues LLMs build geometric memory maps. Evals live in a separate section.
Swarm Inference details: frontier-level quality with 3–30 nodes, 2–5× compute overhead
Fortytwo’s decentralized “Swarm Inference” adds new operational color: accuracy climbs quickly from 3 to 7 nodes and plateaus around ~30, while consensus adds about 2–5× the compute of a single inference and 2–5 seconds of end‑to‑end latency on simple queries scaling notes. Following up on Swarm Inference, which hit 100% on AIME‑2024 and 96.7% on AIME‑2025 via pairwise Bradley–Terry judging, today’s notes also stress robustness, with only a 0.12% drop under distractors versus ~6.20% for single models benchmarks summary.
- Pairwise head‑to‑head selection plus reputation weighting consistently outperforms majority vote; implementation and data sources are outlined in Fortytwo’s overview and paper project page, and the ArXiv preprint ArXiv paper.
Implicit chain‑of‑thought makes Transformers learn 4×4 multiplication perfectly; standard FT fails
A joint MIT–Harvard–DeepMind study shows a small Transformer trained with implicit chain‑of‑thought (ICoT) reaches 100% on 4‑digit‑by‑4‑digit multiplication, while standard fine‑tuning collapses to ~1% accuracy paper summary. Mechanistic probes suggest the successful model builds a running‑sum/carry circuit via tree‑like attention, stores pairwise digit products in earlier tokens, and uses a compact Fourier‑style digit code; a small bias head that predicts the running sum helps overcome the long‑range dependency pitfall mechanism notes.
Google preprint: LLMs form geometric memory maps that turn multi‑step pathfinding into one‑shot picks
A Google preprint argues LLMs can build a global geometric map from only local relation pairs, enabling them to collapse multi‑step pathfinding into a single selection when the knowledge is in weights—yet they fail when the same facts are provided only in context paper thread. The authors suggest a natural training bias induces this map‑like memory and that there’s room to make memory more explicitly geometric for stronger planning paper link.
- Full technical details and experiments are available in the manuscript ArXiv paper.
ByteDance’s Ouro looped reasoning now runs on vLLM nightly, bringing efficient latent loops to serve
Looped LMs (Ouro) introduce an additional scaling axis—iterating internal latent reasoning before emitting tokens—and are now runnable on vLLM’s nightly builds, easing deployment of this paradigm in standard inference stacks inference update. The approach aims to improve reasoning quality without proportionally growing model size by letting the network “think in loops” and aggregate intermediate traces before finalizing outputs.
⚖️ Courts and platforms test AI boundaries
Two impactful legal threads: UK High Court mostly favors Stability AI vs Getty on training claims (narrow TM issues remain); Perplexity alleges Amazon seeks to block AI assistant shopping flows. Safety ethics handled elsewhere.
UK court backs Stability AI on training legality; watermark trademark issue persists
The High Court of England and Wales dismissed Getty’s secondary copyright claims against Stability AI, finding model weights/outputs are not reproductions under CDPA §§17, 22–23; passing off and most trademark claims were rejected, with a narrow trademark win limited to synthetic watermarks in older SD versions judgment summary. Commentary from Stability’s former CEO frames this as a major precedent for UK training legality while noting a US case still looms founder comment, with additional recaps reinforcing the split outcome case recap.
Perplexity alleges Amazon move to block AI assistant shopping on its platform
Perplexity claims Amazon sent a legal notice demanding it prevent Comet users from using AI assistants to search and purchase on Amazon, and vows to continue supporting user choice; the company published its position and examples of the targeted workflows company statement, with detailed arguments in its blog post Perplexity blog post. Independent coverage highlights the broader platform‑access implications for agentic commerce feature brief.
arXiv clamps down on AI‑generated paper spam in computer science
arXiv will no longer accept computer‑science review or position papers unless authors prove prior peer review, a response to the surge of low‑effort AI‑generated manuscripts overwhelming moderators policy change. Separate commentary notes the change targets bots while preserving the preprint server for original research policy thread.
Japanese IP group presses OpenAI to halt training and outputs tied to its members’ works
Japan’s Content Overseas Distribution Association, whose members include Studio Ghibli, Bandai Namco, and Square Enix, argues that copying for machine learning without prior permission may violate Japanese copyright law and criticizes opt‑out schemes; it asks OpenAI to stop both training on and outputting content referencing their IP, citing Sora 2 examples CODA complaint. The push underscores rising cross‑border pressure on AI training norms, distinct from recent UK rulings.
💼 Enterprise signals: Claude Code credits, AI pivots, traffic scale
Adoption and demand signals: Anthropic grants temporary Claude Code credits (Max $1,000; Pro $250) to spur trials; IBM trims headcount to lean into AI/software; Similarweb shows ChatGPT nearing 6B monthly visits. Product features covered elsewhere.
Anthropic gives Claude Code users temporary credits: $1,000 Max, $250 Pro until Nov 18
Anthropic is temporarily adding free usage credits for Claude Code on the web and mobile—Max subscribers get $1,000 and Pro $250—separate from normal limits and expiring Nov 18, to spur hands‑on trials of cloud coding workflows Credits announcement, with the entry point at Claude Code page.
The move lowers switching costs for long‑running or compute‑heavy tasks (plan on web, finish in CLI) and should surface real usage data to guide pricing and product fit Usage advice.
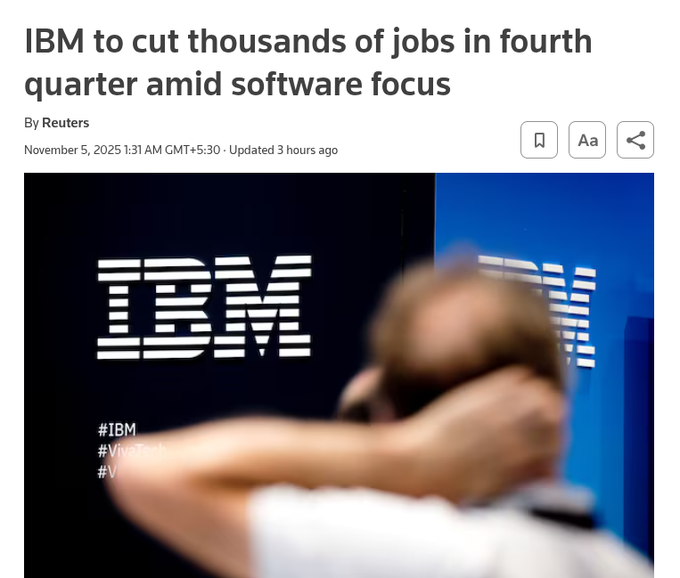
IBM to cut a low single‑digit percent of ~270k roles in Q4 to pivot harder into AI‑software
IBM plans Q4 layoffs affecting a low single‑digit percent of its ~270,000 workforce, aligning costs with higher‑margin software and AI‑linked cloud demand after Q3 showed Red Hat/cloud growth slowing from 16% to 14% Reuters summary.
For AI leaders, the signal is clear: legacy services are being trimmed to fund AI‑centric revenue lines and operating leverage.
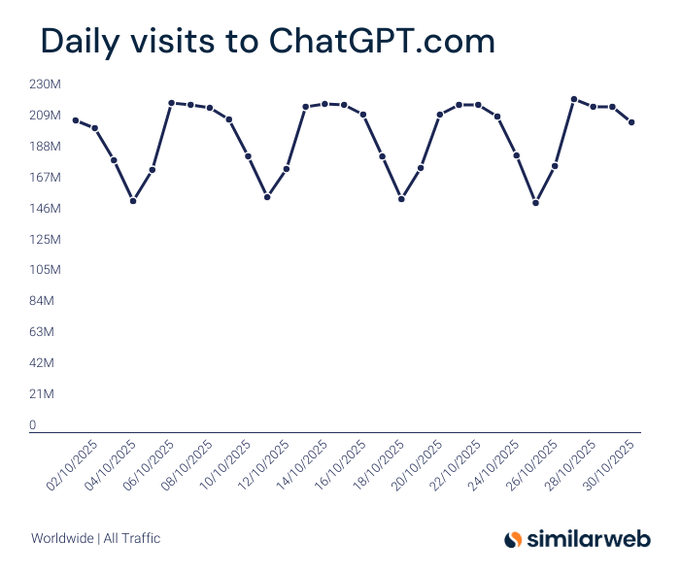
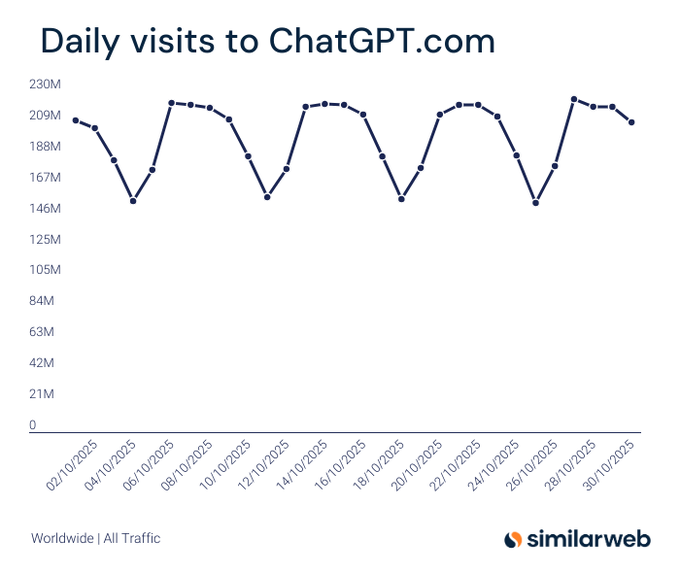
Similarweb: ChatGPT’s daily visits swung ~150–220M in Oct; 6B monthly within reach
Fresh Similarweb slices show ChatGPT’s daily traffic fluctuating roughly 146–218M through October, implying a run‑rate near the 6B monthly visits milestone Daily visits chart, following up on traffic scale that placed ChatGPT just shy of 6B for the month. The scale underscores durable consumer pull that can translate into steady enterprise lead flow and model feedback cycles.
🎬 Creative stacks: Sora on Android, try‑ons, video arenas
Lots of consumer‑facing gen media updates: Sora expands to Android regions; Perplexity adds iOS ‘Virtual Try On’; NotebookLM preps custom video styles; Vidu Q2 ranks in video arenas; ByteDance video upscaler pricing; Grok adds Upscale. Engineering‑oriented.
Sora lands on Android across seven regions; official X handle goes live
OpenAI’s Sora app is now available on Android in the US, Canada, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, and Vietnam, with testers already asking for APKs; the app also launched an official X presence. This expands Sora’s distribution beyond iOS and signals broader mobile video‑gen adoption timelines Android availability, APK chatter.
For teams building creative pipelines, broader device reach matters for feedback loops, content capture, and real‑world latency testing prior to SDK integrations; watch for region gating and rate‑limit differences as early signals of serving readiness official handle.
Vidu Q2 debuts at #8 in the Video Arena; 1080p/8‑second, multi‑reference control
Vidu Q2 launched with 1080p 8‑second generation, ranking #8 on Artificial Analysis’ Text‑to‑Video leaderboard; it supports multi‑image reference control and is priced at ~$4/min (Turbo) and ~$6.10/min (Pro), slotting between Hailuo 02 Pro and Veo 3.1 and slightly below Sora 2 pricing leaderboard brief, video arena.
• Useful for teams needing controllable identity/shot consistency without heavy rigging; consider reference‑set curation and temperature policy to balance fidelity vs. motion smoothness.
• Pricing and rank positioning imply trade‑offs ideal for short promo loops, character‑consistent clips, and batch ad variants.
fal hosts ByteDance Video Upscaler: 1080p/2K/4K at ~$0.0072 per second
fal added ByteDance’s Video Upscaler with 1080p, 2K, and 4K outputs, 30/60 fps support, and pricing around $0.0072 per second for 1080p, providing a low‑cost finishing pass for AI‑generated footage or denoised captures pricing note.
At this cost‑point, pipeline design can standardize on faster base generation (lower native res) and rely on deterministic upscale late in the chain; benchmark for temporal artifacts across scene cuts and motion‑blur regions before production extrusion.
NotebookLM is adding custom style prompts for Video Overviews; ties to Nano Banana 2
Google is working on “Custom Styles” for NotebookLM Video Overviews, letting users define a visual style directly via prompt text (e.g., storybook vs. photoreal). The update likely coincides with Google’s next native image model (Nano Banana 2 / GEMPIX‑2) based on fresh Gemini site cues NotebookLM post, Nano Banana 2 post.
Engineering takeaways: explicit style control reduces prompt‑tuning churn, improves batch consistency for templated video, and is a clean surface for A/B testing editorial tone against watch‑time/retention metrics.
Perplexity adds iOS Virtual Try On with full‑body AI avatars for shopping
Perplexity rolled out a “Try on” feature in its iOS app that generates full‑body AI avatars so users can visualize apparel on themselves; initial availability appears US‑only and leverages recently acquired VTO tech feature article.
For retailers and agents, this is a useful case study in pairing image synthesis with commerce flows (catalog constraints, fit consistency, safety around body imagery) and in measuring funnel uplift from AI visualization to checkout.
🎙️ Realtime voice agents and expressive TTS
Voice systems news: Together AI pushes end‑to‑end realtime voice (streaming Whisper + TTS + serverless hosting); ElevenLabs voices coach Chess.com’s Play Coach; open‑weight Maya1 claims sub‑100ms, 1‑GPU expressive voice. Few pure ASR/TTS papers today.
Together AI ships end-to-end realtime voice stack with streaming Whisper and sub-second TTS
Together AI rolled out an integrated stack for realtime voice agents: streaming Whisper STT with end‑of‑speech detection, sub‑second TTS (Orpheus, Kokoro), WebSocket streaming, and serverless hosting for open‑source TTS—designed to scale from 10 to 10,000 concurrent calls realtime voice stack, platform brief, feature details, Together blog post. • Stack highlights: EoS‑aware STT for timely turn‑taking, low‑latency TTS voices, and infra tuned for sustained concurrency—all crucial for voice copilots, call centers, and in‑app assistants.
Maya1 open-weight voice model runs on one GPU with <100 ms latency and 20+ emotions
Maya Research released Maya1 (3B params) as an open‑weight expressive voice model claiming sub‑100 ms latency, >20 emotions (e.g., laugh, whisper), and single‑GPU deployment; it targets real‑time assistants and character voices with inline emotion tags and streaming via SNAC model announcement, Hugging Face page. The combo of low latency and modest hardware makes it attractive for on‑prem and edge voice agents.
ElevenLabs voices power Chess.com’s Play Coach with Carlsen, Hikaru and Levy likenesses
Chess.com’s new Play Coach mode features authentic‑sounding voices for Magnus Carlsen, Hikaru Nakamura, and Levy Rozman, tuned for pacing and vocabulary in collaboration with the talent—an example of celebrity‑calibrated TTS for education and coaching agents Chess.com coach voices. For AI builders, it’s a template for licensed, persona‑aligned voice experiences that improve engagement without sacrificing latency.