Kosmos AI Scientist posts 79.4% accuracy, 1,500‑paper runs – Google tests Co‑Scientist
Stay in the loop
Free daily newsletter & Telegram daily report
Executive Summary
Edison Scientific launched Kosmos, an autonomous “AI Scientist” that turns long‑horizon literature‑to‑code research into auditable runs tied to code and citations. It reports 79.4% audited conclusion accuracy — the kind of throughput that turns compute into publishable work.
Beta users say a 20‑step run replaced months of expert effort, scaling linearly with depth. And Google is pushing the same pattern: Gemini Enterprise is piloting a “Co‑Scientist” that tournament‑ranks ~100 ideas in ~40 minutes against an explicit rubric, while NotebookLM’s new Deep Research browses hundreds of pages and compiles a cited report.
A timely 94‑page survey argues for closed‑loop agents that plan experiments, call tools, and grade their own steps. If you pilot this wave, set budget guardrails and log every step.
Feature Spotlight
Feature: AI‑accelerated science and research agents
AI research agents arrive: Kosmos claims single‑run synthesis of ~1.5k papers + 42k LOC with auditable outputs, while Google tests a 40‑min multi‑agent Co‑Scientist that ranks ~100 ideas per run; NotebookLM adds Deep Research reports.
Cross‑account surge around autonomous research: Kosmos “AI Scientist,” Google’s Gemini Enterprise Co‑Scientist, and NotebookLM’s Deep Research. Engineers care because these systems operationalize long‑horizon workflows with auditable traces and tournament‑style idea selection.
Jump to Feature: AI‑accelerated science and research agents topicsTable of Contents
🔬 Feature: AI‑accelerated science and research agents
Cross‑account surge around autonomous research: Kosmos “AI Scientist,” Google’s Gemini Enterprise Co‑Scientist, and NotebookLM’s Deep Research. Engineers care because these systems operationalize long‑horizon workflows with auditable traces and tournament‑style idea selection.
Kosmos “AI Scientist” debuts with audited outputs and expert‑level throughput
Edison Scientific unveiled Kosmos, an autonomous research system that can synthesize ~1,500 papers and write ~42,000 lines of analysis code in a single run, with 79.4% conclusion accuracy and full traceability to code and citations Altman endorsement, Launch article. The team highlights seven example discoveries and a structured world‑model approach that lets the agent stay on‑objective over millions of tokens.
- Beta users report a single 20‑step run replaced about 6.14 months of expert work, with perceived work scaling linearly with run depth scaling chart.
Why this matters: Kosmos packages long‑horizon research into repeatable, auditable workflows. That’s the piece lab leads and R&D heads need to justify compute and compliance at the same time.
Gemini Enterprise “Co‑Scientist” runs tournament rankings to refine research ideas
Internal strings and demos show Google piloting two multi‑agent flows inside Gemini Enterprise: Idea Generation and a Co‑Scientist that, per run, spends ~40 minutes to generate and tournament‑rank ~100 ideas against user‑set criteria feature leak, Feature brief. The 3‑step loop takes a research goal + data, spawns specialist agents to explore, then evaluates and ranks based on an explicit rubric.

Why this matters: Teams get a repeatable front‑end for directed ideation with built‑in evaluation, which is the bottleneck for scaling literature triage and hypothesis pruning across orgs.
NotebookLM “Deep Research” turns broad web sweeps into structured, cited reports
Google rolled out a Deep Research mode in NotebookLM that can autonomously browse hundreds of pages, synthesize findings into a structured report, and attach an annotated source list; it also expands supported source types (e.g., Drive URLs, Sheets, images) for mixed‑media research sets feature demo, Google blog post. Early user tests call it an “outstanding learning tool,” noting integrated mind maps, flashcards, and quizzes for follow‑up study hands‑on notes.

Why this matters: This is a ready‑to‑try research assistant with long‑running retrieval and auditable outputs—useful for product reviews, policy scans, and backgrounders that used to take days.
Survey catalogs scientific LLMs and argues for agent loops tied to real evidence
A comprehensive survey of scientific LLMs compiles 270 datasets and 190 benchmarks, proposes a taxonomy spanning raw observations→theory, and tracks a shift from single‑turn quizzes to process‑based grading of steps, tools, and intermediate results paper thread, ArXiv paper. The authors advocate closed‑loop agents that plan experiments, call simulators or labs, validate outcomes, and update shared knowledge—framing how to train and evaluate systems beyond static corpora.
Why this matters: It’s a roadmap for engineers stitching models, tools, and evaluators into credible pipelines for scientific work, with benchmarks that reward the process—not just the final answer.
🏭 AI factories, datacenters and ops wins
Infra stayed hot: NVIDIA’s Jensen framed custom ASICs vs ‘AI factories’, Groq opened a 4.5MW Sydney site, and OpenAI reclaimed ~30k CPU cores via a logging tweak. Also posted: H200/B200 price trends and DRAM/VRAM squeeze. Excludes research‑agent launches (covered as feature).
NVIDIA’s Jensen dismisses custom ASICs as “science projects,” touts AI factories
At a UBS Q&A during GTC, Jensen Huang argued that customer ASICs can’t match NVIDIA’s full‑stack “AI factory” approach, citing an internal roadmap claiming up to ~40× beyond Hopper and the ability to place $100B‑scale POs with end‑to‑end systems and supply chain confidence transcript highlights. For infra leads, the message is clear: buyers will be sold on time‑to‑revenue, not chip lists.

This frames procurement around platform certainty and execution risk. If you’re modeling long‑lead data center bets, build scenarios where ASIC options don’t materially lower TCO once software, networking, power, and delivery timelines are included.
OpenAI frees ~30,000 CPU cores by disabling a costly Fluent Bit path
OpenAI’s observability team profiled node‑level Fluent Bit and found fstatat64 calls (triggered by inotify) burning ~35% CPU; turning that path off returned ~30,000 CPU cores to Kubernetes clusters processing nearly 10 PB/day of logs talk recap, with methodology and impact shared in the KubeCon session KubeCon talk. This is a big ops win: same workload, half the CPU.
If you run Fluent Bit, replicate the perf tracing, test inotify behavior under heavy appenders, and stage a rollout behind feature flags. Savings at this scale can fund more inference capacity immediately.
Groq opens 4.5MW Sydney site to serve APAC with local inference
Groq lit up a 4.5MW data center in Sydney in partnership with Equinix Fabric, bringing low‑latency token serving to Australia and the wider APAC region launch note, with details in the company’s release press post. For teams in Australia, this cuts cross‑ocean latency and can lower per‑request costs when routing to closer endpoints.
Expect regional routing policies and capacity reservations to matter. If you’re piloting Groq, test latency deltas from Sydney versus US/EU regions and adjust traffic shaping accordingly.
H200/B200 pricing spikes at launch, steps down later but stays elevated
Morgan Stanley exhibits circulating today show rental pricing for 8× H200 and early B200 nodes surging at launch, then stepping down as supply ramps—yet not returning to prior baselines chart thread. The takeaway for capacity planners: scarcity premiums ease, but structural demand keeps floor prices higher than last gen.
Model budgets around staged price relief, not a full reversion. Lock short terms for the peak window; renegotiate as additional capacity lands.
RAM/VRAM prices reportedly tripling in months amid AI server demand
A widely shared Gamers Nexus breakdown reports DRAM pricing up ~3× in recent months, with knock‑on effects for NAND and GPU VRAM as AI servers absorb supply; prior oversupply cuts and potential manufacturer coordination are cited as drivers video note, echoed by community commentary flagging lab lock‑ins market note. This affects both server buildouts and on‑device edge AI plans.
Budget buffers for memory should widen. When speccing clusters or local inference nodes, watch lead times and consider pre‑buys on DIMMs/VRAM‑heavy SKUs before the next allocation bump.
🛠️ Agentic dev tooling and coding workflows
New posts focused on building/operating agents: Deep Agents patterns in LangGraph, Claude Code on Windows, NVIDIA’s Bash computer‑use agent tutorial, OpenCode’s architecture, and CLI ergonomics. Excludes research‑automation (see feature).
Claude Code gets a one‑line Windows installer (no WSL)
Anthropic’s coding CLI runs on Windows with a single command, shown installing Claude Code v2.0.35 without WSL: curl -fsSL https://claude.ai/install.cmd -o install.cmd && install.cmd && del install.cmd Windows install. This lowers setup friction for enterprise laptops and lab machines; grab the script directly if you need to audit it first installer script.
LangChain formalizes “Deep Agents” with planning, sub‑agents and memory
LangChain outlined Agents 2.0 (“Deep Agents”) patterns that turn brittle single‑loop agents into orchestrated systems with explicit planning, specialist sub‑agents, and persistent memory built on LangGraph framework explainer. Teams get clearer state control, recoverability, and tool hand‑offs for long, multi‑step tasks.
Amp CLI adds --mode to steer how the agent executes
Sourcegraph’s Amp now supports amp -m <mode> (e.g., rush, free) so you can control execution style from the command line for repeatable CI and local runs cli update. This lands after context management, where Amp shared concrete patterns to keep agent context stable across edits; the flag helps lock behavior for reproducible diffs.
mcporter compiles a Remote MCP server into a ready‑to‑run CLI
With one command, npx mcporter generate-cli --compile, you can turn a remote MCP server (e.g., deepwiki) into a signed, runnable CLI that bundles tools and flags for offline or scripted use cli example. Good for locking versions, isolating access, and handing teammates a zero‑setup binary MCP docs.
NVIDIA shows a Bash “computer‑use” agent built with LangGraph
NVIDIA’s tutorial walks through building a natural‑language→Bash agent using LangGraph’s create_react_agent(), with safety guardrails and a production‑ready path in under an hour tutorial overview. It’s a crisp example of tool‑use orchestration for shell automation and ops runbooks.
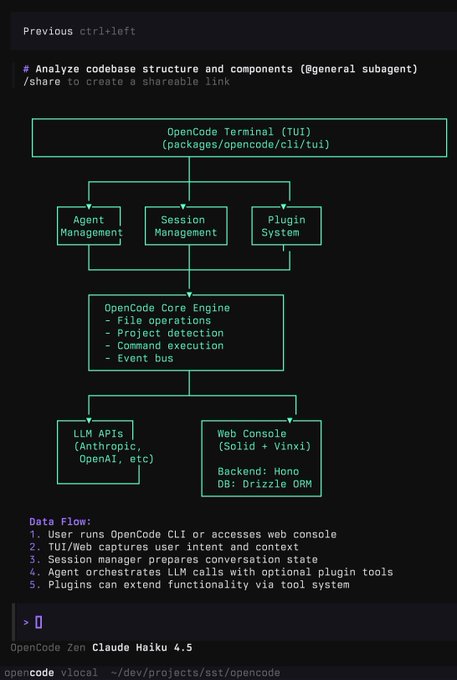
OpenCode previews a full‑stack agent TUI with plugins and a web console
An early look at OpenCode shows a terminal UI and a web console layered over an engine with agent/session management, a plugin system, file ops, project detection, and command execution, wired to Anthropic/OpenAI APIs; the backend uses Hono and Drizzle ORM architecture diagram. This is aimed at teams standardizing dev workflows around agent runs and traceability.
LangGraph “Swarm” demo ships an Article Explainer multi‑agent tool
A community Article Explainer uses LangGraph’s Swarm architecture to coordinate specialists that parse PDFs, generate explanations and analogies, extract code, and run security passes in one chat UI project page. It’s a practical blueprint for multi‑agent division of labor on technical documents.
🔭 Gemini 3 watch: pre‑release signals and strings
A fresh wave of Gemini 3 chatter and app strings; today’s items add UI text linking “3 Pro” image creation to a newer Nano Banana, daily gemini‑cli upgrades, and tester anecdotes. Excludes Co‑Scientist/Deep Research (covered as feature).
App strings tie Gemini 3 Pro image creation to Nano Banana 2
New UI text says “Try 3 Pro to create images with the newer version of Nano Banana,” and a companion string claims 3 Pro and Nano Banana 2 will be released together strings screenshot. This tightens the expectation that Gemini 3 Pro will ship alongside an upgraded image stack, following up on Vids leak that showed a “powered by Gemini 3 Pro” label inside Google Vids.
Signals converge on Gemini 3 next week; gemini‑cli is updating daily
Multiple trackers now expect a Gemini 3 launch next week, with chatter that Nano‑Banana 2 and possibly Veo 4 could land alongside it; developers also note the gemini‑cli has seen noticeable upgrades almost daily as Google preps for release timing thread, release rumor. One tester even reports a stealth appearance on mobile via the Canvas feature, hinting at staged rollout activity mobile sighting.
Early tester: Gemini 3 links the “perfect” YouTube Short to answer a query
An early‑access anecdote says Gemini 3 can respond by attaching an exact YouTube Short that answers the question, suggesting tighter retrieval/tooling across video content than prior models tester note. For product teams, that points to richer, source‑grounded replies in consumer help, education, and support flows.
Community asks what backs Gemini 3 hype versus GPT‑5 Pro
Engineers question why the community is so sure Gemini 3 will beat current leaders and ask for concrete backing beyond teaser buzz and anecdotes comparison question. Some testers remain optimistic, calling the rumored model a potential “banger,” but details on evaluators, tool use, and pricing remain to be seen anticipation post.
📊 Benchmarks and how to measure agentic work
One concrete leaderboard update plus a meta‑discussion on evals: Design Arena now topped by GPT‑5.1 variants, while multiple threads urge shifting beyond answer accuracy to agent brittleness, doom loops, and planning errors.
Calls grow to benchmark agents for brittleness, doom loops and tool use
Multiple threads argue today’s scores don’t capture economic value because they measure single‑shot answers, not whether agents plan, recover, and use tools well—coming after ML/HPC leaderboard showed agents slower than expert humans. Ethan Mollick critiques “fictional vending machine” tests and pushes for diagnostics that expose vision mistakes, repeated failure loops, and prompt‑intent misses benchmark critique, eval gap thread, why failures, brittleness call. His “job interview” method suggests domain‑specific, hands‑on trials to see if a model generalizes beyond canned benches interview article, with details in the linked guide article.
The point is: build evals that grade process, not just final answers. Include step logging, tool‑call traces, and rubric‑based judgments so you can see where planning breaks instead of only whether the last token looked right agentic measures thread.
A practical eval recipe: criteria, application, and automation for verifiability
Shreya R. outlines a pragmatic eval stack: (1) define a clear rubric for success, (2) specify how to apply it consistently, and (3) automate it at scale—framing “verifiability” as an evaluator design problem rather than a property of the task itself evals framework thread. That pairs well with Karpathy’s Software 2.0 lens that progress accelerates where outcomes are easy to verify (code, math), so your harness matters as much as your dataset verifiability argument.
Actionable takeaway: for agent tasks, write sound rubric functions (compiles, runs, answers), build a stable harness (sandboxed tools, state mgmt), and watch for criteria drift by periodically re‑scoring a human‑labeled slice.
GPT‑5.1 variants dethrone Claude on Design Arena
Design Arena’s community leaderboard now shows GPT‑5.1 (High) on top with an Elo ~1374, edging other GPT‑5.1 variants and pushing Claude 4.5/Opus off the summit benchmarks chart. For teams that rely on Design Arena as a proxy for UI/UX and structured instruction quality, this is a fresh signal to retest prompts and toolchains against GPT‑5.1 tiers.
Two quick checks pay off: compare GPT‑5.1 High vs Medium on your agent prompts, and confirm your post‑processors handle its more verbose rationales the board tends to reward.
🔋 Local inference efficiency: Intelligence‑per‑Watt
A Stanford×Together study proposes IPW as a unified metric and profiles 1M queries across 8 accelerators. Findings highlight 5.3× IPW gains since 2023 and large savings from hybrid local+cloud routing.
IPW study: local LLMs cover 88.7% of queries; 5.3× efficiency gain, hybrid saves ~60%
Stanford and Together propose Intelligence per Watt (IPW = accuracy ÷ power) and profile 1M real‑world queries across 8 accelerators; local models solved 88.7% of single‑turn prompts and IPW improved ~5.3× since 2023 (≈3.1× model gains, 1.7× hardware) overview thread, efficiency details. Hybrid routing—keeping ~80% of traffic local—cuts energy/compute/cost ≈60% (≈45% at 60% routing), with Apple’s M4 Max cited running a 120B local model efficiently routing results, study scope, and full methods in the paper ArXiv paper.
🗂️ Retrieval & document AI pipelines
Practical retrieval and parsing advances: Gemini File Search docs circulate with code paths, while posts dig into OlmOCR2’s RLVR unit‑test rewards and HF’s updated OCR model guide. Excludes NotebookLM Deep Research (feature).
Gemini File Search docs land with code for stores, uploads, and grounded answers
Google’s Gemini File Search now has a clear API how‑to covering store creation, direct file uploads vs Files API imports, async status polling, and grounding model responses against indexed content API docs, with first‑party examples in the docs Gemini file search. Following the free tier launch touted as “RAG in a box,” a Googler also demoed a support bot built on File Search plus Google Cloud Search, signaling real workflows beyond samples Docs bot demo.
- Test both upload paths (direct vs Files API) and verify import status before prompting; the docs show the exact request/response shapes API docs.
- Start small with a single store per domain and add Search grounding only where needed to keep costs predictable Gemini file search.
OlmOCR‑2 uses deterministic unit tests (RLVR) to score parsing runs at scale
A weekend read breaks down how OlmOCR‑2 automates rewards: use a strong model (Sonnet) to scaffold HTML and generate per‑document unit tests, then train the parser with RLVR using pass rates as rewards—no human labels needed Paper notes. The figure shows page‑level rewards as the fraction of tests passed, a practical recipe teams can replicate for invoices, tables, and forms Paper notes.
- Adopt the scaffold→tests→reward loop to bootstrap domain parsers; start with deterministic checks (selectors, totals).
HF’s OCR guide adds new models and when‑to‑finetune guidance for document AI
Hugging Face refreshed its practical OCR playbook—now covering models like Chandra and OlmOCR‑2, when to run out‑of‑the‑box vs fine‑tune, open datasets, and local vs remote serving tips Blog update, with the full write‑up here Hugging Face blog. For teams stitching RAG over PDFs, it’s a concise decision map to improve transcription, layout awareness, and document QA.
- Benchmark OOTB first; fine‑tune only where structure (tables/forms) fails consistently on your corpus.
TeaRAG’s agentic RAG keeps accuracy while cutting tokens by ~60%
A new agentic RAG framework, TeaRAG, compresses retrieval into fact triplets and a knowledge‑association graph, then prunes context with Personalized PageRank; across 6 benchmarks it cuts output tokens by 61% and 59% while raising exact match by 4% and 2% Paper summary. It also trains with process‑aware preference optimization to favor evidence‑aligned, fewer‑step reasoning.
- Route long‑form QA through triplet graphs to shrink model context; measure EM and tokens per answer in the loop.
💼 Enterprise adoption, pricing and ROI
Signals on AI in orgs: Meta formalizes “AI‑driven impact” in 2026 reviews, leaders argue agent pricing should track productivity lift, and Gmail’s smarter scheduling is cited as low‑friction ROI.
OpenAI reclaimed ~30,000 CPU cores by disabling a hot Fluent Bit path
OpenAI’s observability team profiled node‑level logging and found fstatat64 calls (triggered via inotify) dominated CPU in Fluent Bit. Turning that off halved CPU for the same log work, returning about 30,000 cores to Kubernetes clusters that process ~10 PB/day of logs talk summary, with the walkthrough posted publicly YouTube talk. The lesson: profile before you scale; one default can be very expensive.
Local–cloud routing shows up to ~74% compute cost cuts and ~80% energy savings
Stanford and Together introduced “Intelligence per Watt” and found hybrid routing that keeps easy queries local can drop energy use by up to 80.4% and compute cost by up to 73.8%, with ~60% savings even at 80% routing accuracy metric overview. The paper covers 1M real queries across 20+ local models and 8 accelerators; IPW improved ~5.3× from 2023–25, and coverage for creative tasks exceeds 90% on local hardware ArXiv paper.
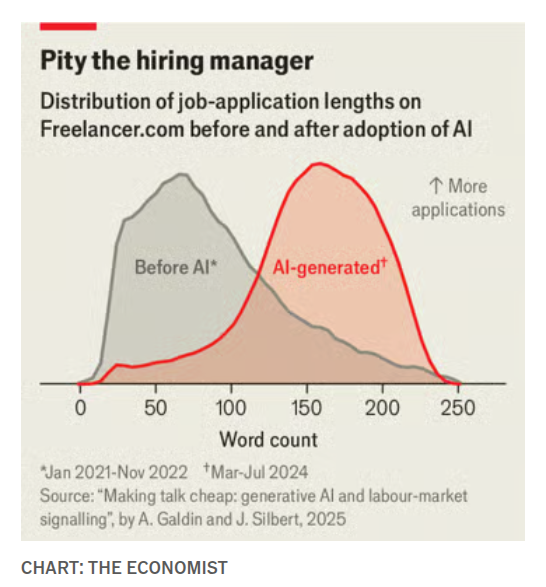
Study: AI‑written proposals erode signals; contractor wages drop ~5%
On Freelancer.com, LLM tools made applications longer (median ~79→~104 words), blurring effort signals that used to correlate with quality; the study estimates roughly a 5% decline in wages and ~1.5% lower hiring versus a no‑AI counterfactual study summary. For teams, this warns that “cheap talk” can degrade screening funnels unless you adjust rubrics and tests.
AI agent pricing should track ROI, not SaaS seat caps
Box’s Aaron Levie argues agent pricing should be tied to productivity lift (e.g., paying ~10% of an engineer’s comp if output doubles) rather than the legacy $10–$50/user SaaS ceiling pricing argument. The point is: when agents drive measurable throughput, budgets follow outcomes, not per‑seat norms.
Calls grow to benchmark agentic work, not just one‑shot answers
Ethan Mollick and others argue we over‑index on single‑turn benchmarks and under‑measure what drives economic value: tool use, planning, recovery when wrong, and brittleness under change agent eval gap. Critiques point out that demo tasks like “vending machines” don’t reveal why agents fail (vision, doom loops, stuck retries) vending bench critique, and demand WHY‑failure diagnostics alongside accuracy failure reasons. For practical guidance on assessing model fit, see the proposed “job interview” approach for AIs evaluation essay.
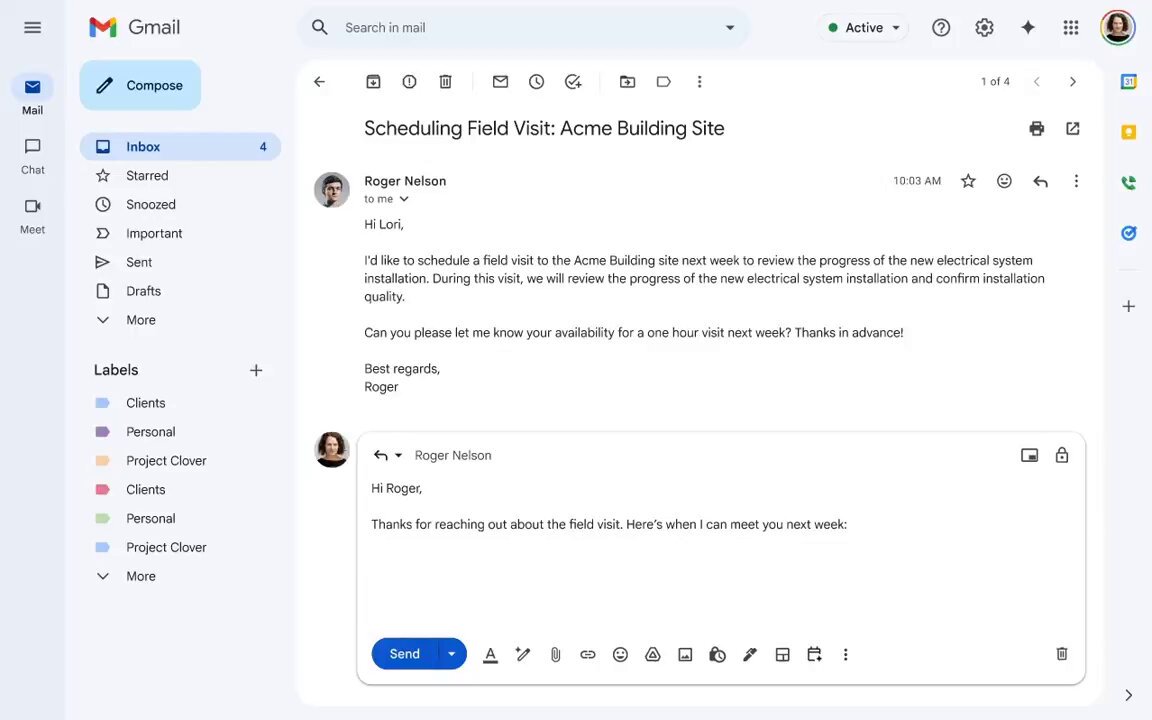
Gmail adds context‑aware scheduling that proposes times and auto‑books
A new Gmail scheduling flow parses email context to suggest viable times and auto‑creates a calendar event once the recipient chooses a slot, removing the classic back‑and‑forth feature demo. A follow‑up shows it avoids blind free‑time dumps and handles the event creation step end‑to‑end feature details.
🧠 Reasoning dynamics and verifiability
Conceptual and empirical pieces: Karpathy’s “verify > specify” framing resurfaces; a paper dissects entropy collapse in RL for reasoning and a long thread formalizes verifiability via rubric→application→automation.
Karpathy: Software 2.0 automates what you can verify, not what you can specify
Andrej Karpathy argues the strongest model for AI’s economic impact is verifiability: tasks with resettable, rewardable, and efficiently repeatable practice loops (math, code, formal puzzles) will surge, while non‑verifiable creative/strategic work lags Karpathy thread. For engineering leaders, that means roadmaps should favor problems where you can build an automated evaluator and let systems "practice" at scale.
RL for reasoning: entropy collapses; 600 curated problems can match ~17k
A new RL‑with‑verifiable‑rewards study shows model entropy collapses as training over‑reinforces a few high‑reward token paths; off‑policy updates and clipping thresholds worsen it, hurting generalization. With careful curation, ~600 good problems can match training on ~17k, and adaptive entropy regularizers plus reweighting positive‑advantage tokens stabilize learning paper summary.
A practical framework: verifiability = rubric, application, automation
Shreya Shankar reframes verifiability as an engineering artifact, not a property of the task: define a success rubric, implement a sound/complete evaluator, then automate it at scale framework thread. The claim: most tasks become verifiable once you faithfully encode correctness—so the bottleneck is building good evaluators, not waiting on smarter models.
Agent eval gap: call for WHY‑failure diagnostics beyond single‑answer scores
Ethan Mollick and others argue current leaderboards miss what matters economically: tool use, recovery from errors, generalization, and brittleness. They call out “fictional vending‑machine” demos, urging evals that test prompt intent, diagnose vision mistakes, and detect "doom loops" when agents repeat failures agent eval point, vending‑bench remark, and job interview post. The takeaway: build harnesses that explain why agents fail, not just whether they answered once.
OlmOCR2 turns parsing into RLVR with LLM‑generated unit tests as rewards
OlmOCR2 outlines a pattern to make semi‑structured tasks verifiable at scale: use a strong model to scaffold HTML and auto‑generate deterministic unit tests per document, then optimize a parser with RLVR against those tests—no human labels required paper notes. This “LLM‑as‑grader” loop is portable to invoices, forms, and other doc QA where the environment is resettable.
TeaRAG trims ~60% tokens while nudging EM up via fact‑graph and process DPO
TeaRAG introduces a token‑efficient agentic RAG: build compact fact triplets, rank them on a knowledge graph, and train with process‑aware DPO to keep reasoning tight. Reported gains: exact match up by up to 4% with ~61% and ~59% fewer generated tokens on two benchmarks paper summary. Following up on DeReC runtime (95% runtime cut for fact‑checking), this shows you can boost fidelity and shrink thinking budgets together.
Survey: scale agents by growing tasks, tools, and verifiers in one G‑E‑F loop
A survey of agent environments formalizes the Generation‑Execution‑Feedback loop: environments must both create diverse tasks and verify outcomes, with dense, hack‑resistant rewards. It highlights the generator vs verifier split and stresses exact checks for code/math vs rubric or reward models for open text survey summary. For builders, the message is to scale tasks, tool access, and evaluators together.
🎨 Creative media: relighting, style LoRAs and demos
A cluster of creator‑facing updates: Qwen‑Edit multi‑angle lighting LoRA, NVIDIA’s ChronoEdit LoRA, ImagineArt v1.5 samples, an AI‑native game art‑direction demo, and a short Grok Imagine clip.
NVIDIA’s ChronoEdit‑14B “Paint‑Brush” LoRA lands with rapid cinematic restyles
NVIDIA published ChronoEdit‑14B Diffusers Paint‑Brush LoRA on Hugging Face, showing near‑instant look/grade shifts on the same shot release demo Hugging Face model. Editors can sweep through color grades and tone patterns without re‑generating full frames.

For art leads, this compresses grading iterations into prompts, keeping direction tight while you explore multiple treatments off a single base.
Qwen‑Edit Multi‑Angle Lighting LoRA ships controllable relighting presets
Qwen‑Edit‑2509 Multi‑Angle Lighting arrived with directional relighting from luminance maps (e.g., front, left‑front, above), letting creators change light on a single still without multi‑view capture release note. The author calls it an early proof‑of‑concept and asks for larger lighting datasets, with a runnable Space for hands‑on tests Hugging Face page and Hugging Face Space.
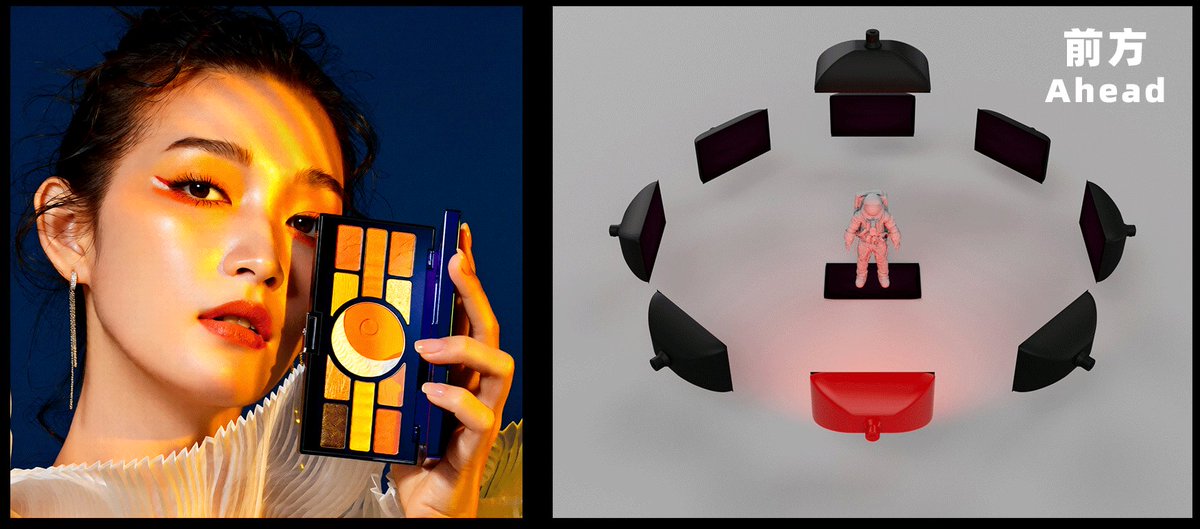
Why it matters: fast, parameterized relighting is a missing dial for product shots, key art, and continuity—this LoRA gives teams a cheap control knob to try today.
AI‑native game demo: one world model drives assets, lighting and camera
A playable demo shows an AI‑native workflow where a single compressed world model controls assets, lighting, and camera—letting one person explore ~50 art directions in an evening game demo. The clip flips styles live, hinting at pipelines where style becomes a parameter, not a rebuild.

Teams making prototypes or vertical slices can trial this for rapid art direction convergence before investing in bespoke assets.
ImagineArt v1.5 release praised for sharper, more lifelike people
Creators report ImagineArt 1.5 is out, citing noticeably sharper renders and more natural, lifelike faces and skin user report, with another post calling the 1.5 drop “genuinely impressive” on realism release note. If you maintain image model shoot‑outs, add 1.5 to your A/Bs—this looks like a quality bump that could displace a default stack.
Grok Imagine micro‑clip shows high‑fidelity macro detail on an opal spider
Following up on creator demos that highlighted lifelike micro‑clips, a new 6‑second “opal spider” sample shows crisp iridescent legs and smooth gradient lighting—good enough for quick promos or social cut‑downs short clip. It reinforces Grok Imagine’s strength at short, striking visuals.

If you need thumb‑stopping B‑roll, this output looks ready to test in content calendars.
🛡️ Safety, identity and governance signals
Identity and governance chatter: Kimi warns of impersonators, Fei‑Fei Li downplays AGI as a scientific term, and reports say Yann LeCun plans to leave Meta while advocating world models over LLMs.
Report: Yann LeCun to leave Meta; calls LLMs a dead end, backs world models
Reports say Yann LeCun plans to exit Meta, criticizing LLMs as a “dead end” and advocating causal world models that plan and act hierarchically with measurable objectives. If confirmed, it signals a high‑profile push toward alternative architectures. report summary Gizmodo report
Moonshot AI warns of Kimi impersonators; confirms official handles
Moonshot AI says only @Kimi_Moonshot and Kimi.com are official and warns that look‑alike accounts such as “Kimi CLI” or “Kimi_Official” are impostors. Teams should verify before engaging or installing tools claiming Kimi branding. brand warning Official site
Fei‑Fei Li says AGI is more marketing than science; parts exist, whole doesn’t
Fei‑Fei Li argues “AGI” is a marketing label, noting we’ve achieved pieces like conversational AI but not the full scientific goal. It’s a reminder to focus on concrete capabilities and evaluation over labels.

🤖 Embodied AI: biped agility and authenticity debate
LimX Dynamics’ TRON 1 biped draws interest for agility and potential voice I/O; a separate thread challenges a UBTech humanoid clip as CGI and calls for proof. Mostly demos, limited stack details today.
UBTech humanoid “warehouse army” clip labeled CGI by critics; community asks for proof
A viral warehouse video showing rows of UBTech humanoids drew immediate pushback, with prominent founders calling it CGI and others asking UBTech for first‑party evidence to verify the scene authenticity thread. This flares just days after factory rollout (Walker S2 deployment, 500 units targeted), raising pressure for auditable footage, on‑site demos, or continuous‑take captures.
So what? Credible proof affects buyer confidence, safety reviews, and hiring. If real, it signals meaningful manufacturing and calibration throughput. If not, customers will demand on‑prem tests before pilots. Either way, engineers should plan evaluation protocols that check continuous operation, untethered runs, and human‑in‑the‑loop safety gates.
LimX TRON 1 biped shows agile locomotion; community asks for voice/assistant I/O
A fresh TRON 1 clip shows confident bipedal movement and quick recovery, prompting calls to add speech and assistant-style control for home use demo thread. LimX bills TRON 1 as a research‑ready platform with modular foot ends and SDK hooks, which makes voice I/O and higher‑level autonomy a practical next step for labs and startups Product page.

Why it matters: If this platform stays stable under real‑world disturbances, the bottleneck shifts from legs to the autonomy stack. Teams can prototype voice grounding, task planning, and teleop→assist transitions on a capable chassis before investing in full humanoid stacks.