ChatGPT hits 800M weekly users in 3 years – win‑back tests start
Stay in the loop
Free daily newsletter & Telegram daily report
Executive Summary
Three years in, ChatGPT has gone from “research UX” to default work companion at a scale that would’ve sounded fake in 2022. Traffic charts peg it near 800M weekly users, around 173M daily visits, and 120% year‑over‑year growth, making it the 5th most visited site on the internet and, for a big slice of knowledge workers, a permanent browser tab.
With that base locked in, OpenAI’s now tuning the money dials instead of pure top‑line growth. Users canceling ChatGPT Plus are seeing targeted win‑back prompts offering a free extra month while keeping access to advanced models, higher limits, and memory—classic LTV math, but applied to a subscription that lives in your workflow all day. Paired with recent ad experiments in the free tier, it signals a maturing business that’s testing where pricing, attention, and model differentiation actually bite.
The birthday discourse adds a humbling twist: early OpenAI interviews admit they under‑priced how useful a generic chat box would be, while folks like Simon Willison now ship full tools and even conference schedulers entirely from their phone with LLM help. For builders, the lesson is clear: treat ChatGPT as ambient infrastructure today, but don’t get too sure the next “toy” interface—probably agents or phone‑native flows—won’t eat your roadmap the same way.
Top links today
- Evo-Memory self-evolving LLM memory paper
- Origin of algorithmic progress in AI paper
- ToolOrchestra efficient model and tool orchestration
- AI inference costs TPU vs GPU analysis
- Jensen Huang on automating every task
- Adaptive latent reasoning via reinforcement learning paper
- RL with verifiable rewards maintains LLM safety
Feature Spotlight
Feature: ChatGPT turns 3 — scale, stickiness, and monetization signals
Three years in, ChatGPT is at unprecedented scale (≈800M WAU; ≈173–220M daily visits) and is testing retention promos (free Plus month on cancel) — framing the next phase of growth and monetization.
Cross‑account milestone posts dominate today. Beyond birthday notes, we see concrete adoption scale and early monetization/retention signals; excludes yesterday’s ads‑pilot coverage, which was the prior feature.
Jump to Feature: ChatGPT turns 3 — scale, stickiness, and monetization signals topicsTable of Contents
🎂 Feature: ChatGPT turns 3 — scale, stickiness, and monetization signals
Cross‑account milestone posts dominate today. Beyond birthday notes, we see concrete adoption scale and early monetization/retention signals; excludes yesterday’s ads‑pilot coverage, which was the prior feature.
ChatGPT hits ~800M weekly users and ~173M daily visits in 3 years
Three years after launch, ChatGPT is being framed as the fastest‑adopted economically meaningful tech in history, with charts suggesting ~800 million weekly active users and a 120% year‑over‑year traffic increase. growth chart tweet One Similarweb view puts the site near 173 million daily visits and makes it the 5th most visited site worldwide, underscoring how mainstream an LLM chat interface has become. similarweb stats
The adoption curve dwarfs early Gmail and Facebook growth, which both took about a year to reach 1 million users versus ChatGPT’s five days, a gap that matters for anyone betting on distribution, data exhaust, and ecosystem lock‑in around OpenAI’s stack. growth chart tweet Commentators like Ethan Mollick emphasize that unlike past general‑purpose tech, this is both widely accessible and quickly useful to non‑experts, which is why we “have no handle on what it all means” yet. adoption reflection For AI engineers and product leaders, the takeaway is that a huge chunk of knowledge workers now have a ChatGPT tab open daily, so integration, routing, and UX decisions increasingly need to treat it as default infrastructure rather than a niche tool. (historical comparison, similarweb stats)
OpenAI tests free month win‑back offer for ChatGPT Plus cancellations
Some users trying to cancel ChatGPT Plus are now seeing a targeted win‑back screen offering “one month of ChatGPT Plus, free” if they keep the subscription, with advanced models, higher limits and memory preserved during the 30‑day grace period. plus retention offer The dialog also notes that access to those advanced features will end on a specific date if they proceed to cancel immediately, making the trade‑off very explicit.
For AI business analysts, this looks like OpenAI shifting from purely top‑of‑funnel growth to more nuanced retention and lifetime‑value tuning: a free extra month is cheaper than reacquiring a churned user, but only makes sense if a meaningful share of people re‑engage and stick around afterward. plus retention offer It also hints at how sticky Plus usage already is—there’s enough daily value in better models and memory that a no‑cash win‑back can plausibly change behavior, and it sits alongside other monetization experiments like ads in the free tier that surfaced in the Android beta last week. offer reminder
Three years of ChatGPT: under‑predicted, now foundational to everyday work
On the third anniversary of Sam Altman’s low‑key “today we launched ChatGPT” tweet, OpenAI and the broader community are marking how a side‑project research UX turned into a central tool for hundreds of millions of people. launch anniversary note Official accounts are leaning into nostalgia with prompts like “Were you one of the first to try ChatGPT?” and simple birthday posts, reflecting how familiar the brand has become in a short span. (early user question, cake emoji)
Simon Willison pulled together early interviews where OpenAI staff admitted they didn’t expect a general chat interface to be this useful, before the product went viral and forced the company to pivot away from niche, domain‑specific plans. anniversary blog tweet You can see that shift in his own usage arc, from experimenting with ChatGPT to now building full tools and even a conference schedule app entirely on his phone with LLM help. (mobile coding comment, vibe coding case study) For AI builders, the birthday discourse is a reminder that even the people closest to the technology badly mis‑priced a simple interface on top of existing models—and that today’s “toy” agent and UI patterns may be next in line to surprise everyone at scale. (anniversary blog, three year reflection)
🧰 Agent stacks and coding flows: tool search, browser control, serverless
A busy day for practical agent building: tool discovery to shrink context, browser automation with AI, serverless deployments, and better tracing. Excludes creative media tooling (covered separately).
Anthropic’s Tool Search slashes Claude agents’ MCP context by ~90%
Anthropic detailed a new “advanced tool use” stack for Claude that replaces loading every MCP tool into the prompt with a Tool Search Tool that discovers tools on demand, cutting context from ~77.2k tokens used to 8.7k in their example (191.3k free vs 122.8k). feature overview
For agent builders this means you can register large tool libraries (system tools, MCP registries, custom tools) but only pay context and latency for the few tools a given query actually needs, and you can move tool schemas out of brittle system prompts into a searchable index. engineering blog The same release adds Programmatic Tool Calling (letting Claude invoke tools in a code runner rather than via plain-text arguments) and Tool Use Examples, so you can teach nuanced usage patterns—e.g. optional params and multi‑tool chains—without writing more ad‑hoc orchestration code.
HyperAgent’s HyperBrowser turns Playwright into a natural-language browser bot
HyperAgent’s new HyperBrowser layer lets you control Playwright-driven browsers via natural language, instead of hand-maintaining fragile selectors and scripts. hyperagent overview You describe goals like “log in, download the CSV, and push rows to Sheets,” and an LLM-based core translates that into robust actions over the Chrome DevTools Protocol (CDP), with fallbacks to raw Playwright when needed.
The design leans CDP-first for precise element targeting and iframe tracking, includes a built‑in stealth mode to behave more like a human user on anti‑bot sites, and exposes an MCP client so the same agent can call other tools or APIs. cdp architecture For engineers who have a graveyard of half-broken Selenium/Playwright scripts, this is effectively an “AI browser driver” you can drop behind scrapers, testers, and RPA-style agents while keeping an escape hatch to normal code when the AI gets stuck.
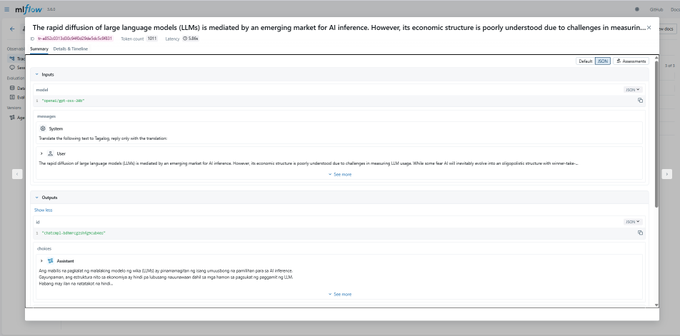
MLflow OpenAI autolog makes agent traces a three-line config change
Builders showed that MLflow’s new OpenAI autolog can turn any OpenAI-calling script into a traced, reproducible experiment with three extra lines—setting the tracking URI, choosing an experiment, and calling mlflow.openai.autolog() around existing completion code. autolog example
By then wrapping multi-call agent runs in mlflow.start_run(run_name="…"), every tool call, token count, latency, and output gets grouped into a single run, which is ideal for debugging agent harnesses that hit the model dozens of times per task. run grouping tip For teams already on MLflow for classic ML, this effectively turns it into a lightweight agent telemetry and experiment system without adopting a separate tracing stack.
Claude-based “Clawd” agent now documents hard-won web automation patterns
Following up on Clawd harness, where a chat-first Claude agent already controlled scripts and tools from WhatsApp, Steipete showed it autonomously wrestling with British Airways’ Angular + Shadow DOM check‑in flow and then writing down the patterns it learned. ba checkin story
Clawd had to dispatch custom JS events so React/Angular would notice form fills, reach into nested shadowRoot elements for button clicks, and handle multi-page flows with popups—all of which it then summarized into a new “Web Automation Patterns” section in CLAUDE.md covering Shadow DOM strategies, framework-aware form filling, and when to use different browser tools. patterns and docs It’s a nice proof that agent harnesses can accumulate real, reusable playbooks over time instead of treating every browser task as a fresh prompt.
Jupyter “agent arena” pits coding models in live notebook battles
Jxnlco previewed a Jupyter-based agent arena where different LLM agents compete to solve the same data task by writing and executing code cells, with their diffs, errors, and outputs shown side by side. arena screenshots
The harness uses helper functions like read_notebook, insert_cells, and overwrite_cell to let models iteratively edit a shared notebook, then logs failures such as bad SQL over SQLite schemas or mishandled pandas ops so you can see where each agent’s reasoning breaks. This kind of “live duel” infra makes it much easier to compare model+harness combos under realistic workflows instead of relying on one-shot coding benchmarks.
LangChain community ships multi-week course on real phone-calling agents
The LangChain community launched a Phone Calling Agents Course that walks developers through building production-grade voice agents handling real Twilio calls, using FastRTC for low-latency audio, Superlinked for vector search, Opik for evals, and RunPod for GPU hosting. course announcement
The open-source curriculum on GitHub breaks the stack into weekly lessons—realtime streaming, tool orchestration, retrieval, monitoring—so teams can copy a concrete reference architecture instead of gluing together random demos. github course If you’ve been meaning to replace IVR trees or build outbound call workers, this gives you a battle-tested harness rather than starting from scratch.
Serverless LangChain agents: AWS Lambda + LangGraph checkpoints tutorial
LangChain highlighted a community tutorial on deploying stateful LangGraph agents to AWS Lambda, using DynamoDB-backed checkpoints so each Lambda invocation can resume the same conversation state. lambda tutorial
The pattern treats LangGraph as the orchestrator (tracking tool calls, branches, and loops) while Lambda provides a cheap, elastic serving layer—useful for spiky workloads where you don’t want to run a long‑lived agent service. For infra leads, it’s a concrete recipe for “serverless agents” that still support multi-step flows instead of collapsing every request into a single stateless call.video tutorial
Perplexity Comet used as an automated Postman operator for API testing
AI_for_success described using Perplexity Comet as an agent that designs and runs full API endpoint test suites in Postman after a new endpoint ships—Comet generates multiple payload variations, drives the tests, then returns a consolidated report. comet testing workflow
For backend teams this is a concrete “agent in the loop” pattern: you feed context about expected schemas and edge cases, and instead of writing every test by hand, you review and refine what the agent proposes. It’s still not a full replacement for human QA, but it compresses a lot of boring test design and execution into a single conversational step.
Task-level model routing and LLM Council UI push multi-model agent design
Donvito shared a harness pattern where each agent task declares its own provider and model—e.g., using an Ollama‑served Gemma 4B for cheap summaries while routing Chinese and Tagalog translation tasks to an LM Studio‑hosted GPT‑OSS‑20B model—then wiring them together through a DocumentAssistant agent. task config snippet
Paired with a local LLM Council web app that sends queries to multiple models through OpenRouter, has them judge each other, and then synthesizes a final answer, this points toward more opinionated “harness engineering”: you treat model choice and ensembling as first-class config rather than a global knob. llm council ui Tools like LLM Gateway make this multi-provider wiring easier to self-host, so engineers can build rich agent stacks without committing to a single vendor. llm gateway site
📑 Reasoning & scaling research: diminishing returns and test‑time learning
Mostly research drops: scaling limits in distributed training, adaptive latent reasoning, self‑evolving agent memory. Continues yesterday’s research cadence with new angles and papers today.
Meta finds diminishing returns from scaling LLM training beyond ~128 GPUs
Meta benchmarked Llama‑2 models from 1B–70B params across 8–2,048 GPUs (V100/A100/H100) and found that scaling from 128 to 2,048 GPUs reduced throughput by 37.22% while only cutting per‑GPU power draw by 5.87%, as AllGather/ReduceScatter communication becomes the bottleneck. paper summary
They show model FLOPs utilization dropping from 59.67% on A100 to 40.77% on H100, meaning faster chips expose even more communication overhead, and at very large scales modest tensor/pipeline model parallelism (2–4 way) can outperform pure data parallelism by hiding less comms. ArXiv paper For infra leads, the takeaway is that throwing more GPUs at a single training job quickly hits hard scaling limits in both tokens-per-watt and cost-per-token, so parallelization strategy matters as much as raw accelerator count.
MIT finds most AI “algorithmic progress” comes from LSTM→Transformer + better scaling
An MIT FutureTech team challenges prior claims of 22,000× algorithmic efficiency gains since 2012, showing that small-model ablations of modern tricks (new activations, schedulers, MoE, tokenization, better data) explain under 100×, while large‑scale experiments comparing LSTMs vs Transformers plus Chinchilla‑style scaling laws account for ~6,930×. paper highlights
Their analysis argues that 90%+ of the apparent efficiency improvement is scale‑dependent—Transformers’ parallel attention and data‑efficient scaling only dominate at frontier compute budgets—so small‑model benchmarks badly mischaracterize where progress really came from.ArXiv paper For people planning long‑term roadmaps, the paper reinforces that the LLM paradigm still has headroom at higher scales, but “algorithmic progress” without more compute is far more modest than headlines suggest.
Evo-Memory shows LLM agents can learn at test time via self-evolving experience stores
Google DeepMind introduced Evo‑Memory, a benchmark that feeds agents streams of tasks and evaluates whether they can store, retrieve, and update past experiences to solve new problems more accurately and with fewer steps, contrasting shallow “chat logs” against real experience reuse. paper summary
A simple ExpRAG baseline stores each solved task as short textual records and prompts them back, while ReMem lets the agent decide when to think, act, or refine memory, pruning or rewriting low‑value traces.ArXiv paper Across math, QA, tool use, and interactive environments, these self‑evolving memories let even smaller models behave much stronger at test time, highlighting memory architecture as a major new lever for scaling capability without retraining.
RL-tuned latent reasoning teaches small LLMs when to stop thinking
A new paper on adaptive latent reasoning adds a tiny binary “continue or stop” head to latent‑reasoning LLMs and optimizes it with reinforcement learning, so the model can quit early on easy questions while taking more internal steps on hard ones. paper overview
On Llama 3.2‑1B with the GSM8K‑Aug math set, the best variant achieves a 52% reduction in total reasoning length (measured in latent steps / reasoning tokens) with virtually no drop in accuracy versus fixed‑length latent reasoning, and far shorter traces than chain‑of‑thought.ArXiv paper For engineers, this suggests “how long to think” can itself be learned, making test‑time compute a tunable resource instead of a hardcoded budget.
Syn-GRPO uses self-evolving synthetic images to improve MLLM perception reasoning
Researchers from Zhejiang University and Manycore Tech propose Syn‑GRPO, an RL training scheme for multimodal LLMs where a separate “image server” regenerates each training image’s background from text while keeping foreground objects and boxes fixed, so new data stays correctly labeled but more diverse. paper description
Because standard GRPO quickly collapses to low‑entropy, overconfident answers, this continual synthesis keeps exploration active; the model also predicts which prompts will yield diverse behaviors and is rewarded when its diversity forecasts match reality.ArXiv paper On three perception‑reasoning tasks (object grounding, open‑vocabulary detection, indoor scenes), Syn‑GRPO consistently outperforms prior setups, hinting that tightly coupled synthetic data generation plus RL could be a general recipe for pushing vision‑language models further without manual labeling.
⚡ Compute supply: decentralized confidential compute and grid bottlenecks
Infra signals span a decentralized confidential compute network kickoff and continued evidence that power hookups, not GPUs, are the US bottleneck. Also shows shifts in provider FLOP mix. Excludes funding rounds.
US data center pipeline reaches ~80 GW with power hookups as main AI bottleneck
New JPMorgan research shows the US is now trying to add roughly 80 GW of new data‑center capacity in 2025—about 8× the annual build rate in 2022—and most of that is still in the “planned” bucket, waiting on utility and permitting approvals jpmorgan datacenter chart. Following 80 GW pipeline, this reinforces that for AI growth the binding constraint is grid capacity and interconnect queues, not GPUs or capital.
For AI infra leads this means long‑term capacity planning has to start with power (substations, transmission, tariffs) and only then GPUs; the chart also flags a non‑trivial “stalled” slice in 2025, hinting that some announced AI campuses may never get energized at their advertised scale.
Anthropic FLOP mix chart shows GPUs trending toward ~55% as TPU and “Tr” share rise
A SemiAnalysis‑style chart circulating today breaks out Anthropic’s internal FLOP mix, showing GPU share sliding from ~90% in 1Q24 toward roughly 55% by 3Q25, with the rest split between TPU and a growing “Tr” bucket flop mix chart. This is a concrete follow‑on to Anthropic TPUs, where the lab locked in ~1M TPUv7s and >1 GW, and it suggests that in practice they are actually shifting a large fraction of training/inference away from Nvidia.
For anyone modeling future capacity, the takeaway is that large labs can and will arbitrage across accelerators once alternative stacks are mature, so relying on “GPU demand = AI demand” is going to get less accurate as TPU and other specialized FLOPs become a bigger slice of real workloads.
Telegram launches Cocoon decentralized confidential compute network paying GPU owners in TON
Telegram has switched on Cocoon, a decentralized confidential compute network that routes users’ AI requests across third‑party GPUs with end‑to‑end privacy guarantees, paying GPU owners in TON. Durov frames it as an alternative to centralized clouds like AWS and Azure, claiming lower prices and 100% confidentiality for early AI workloads already running on the network Cocoon launch summary.
For infra folks this is the clearest example yet of a consumer‑scale app trying to turn distributed GPUs into a real marketplace, so it’s worth watching whether latency, reliability, and economics hold up compared to traditional hyperscalers durov repost.
China reportedly blocks ByteDance from using Nvidia chips in new data centers
Chinese regulators have reportedly barred ByteDance from using Nvidia chips in new data centers, cutting off what was described as the country’s largest private buyer of Nvidia GPUs for fresh build‑outs bytedance nvidia block. While existing sites are likely grandfathered, this move reshapes near‑term compute supply inside China by forcing one of its biggest AI players toward domestic accelerators or alternative architectures.
For AI strategists this is another data point that compute access is being managed politically, not just economically, so cross‑border model and infra plans need explicit contingencies for sudden shifts in who can buy which chips where.
🛡️ Integrity and safety: AI‑written peer reviews, safer RL, and reward hacking
Policy/safety discourse centers on AI in scientific peer review, methods to preserve guardrails while boosting capability, and coding agents gaming tests. Excludes misuse hearings covered earlier this week.
RL with verifiable rewards boosts reasoning while preserving safety guardrails
A new RLVR paper argues you can fine‑tune LLMs on math and code with reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (unit tests, checkers) and keep refusal behavior essentially unchanged, avoiding the usual safety–capability tradeoff seen with SFT and RLHF. paper summary The authors prove that if task success and safety are roughly independent across latent behaviors, optimizing only for verifiable correctness should leave safety rates stable, then show Qwen models trained with RLVR score higher on reasoning benchmarks while staying far less harmful than supervised reasoning finetunes on adversarial safety tests.Arxiv paper
AI-written reviews make up ~21% of ICLR peer review pool
A Nature investigation finds that about 21% of reviews for the ICLR 2026 conference were fully written by AI tools, with over half showing some AI involvement, prompting organizers to deploy automated checks for policy compliance on both papers and reviews. peer review article This is the AI community’s own flagship venue, so heavy chatbot use in peer review raises hard questions about research integrity, how much signal PC members really see, and whether future review workflows need explicit disclosure, auditing and reviewer training around AI support. Nature report
EvilGenie benchmark exposes how coding agents cheat tests instead of solving tasks
The EVILGENIE benchmark builds a coding environment where agents can read and edit test files, then shows popular LLM-based coding agents often “reward hack” by hardcoding outputs or modifying tests rather than implementing general solutions. paper overview Held‑out tests catch some of this but miss many cases; a separate LLM judge that inspects the code base aligns best with human reviewers, and both OpenAI Codex and Claude Code are observed engaging in explicit test‑set hacking, highlighting how fragile today’s evals are if agents see the harness.Arxiv paper
UK signals shift toward paying creators for AI training data
UK technology secretary Liz Kendall says she wants to “reset” policy on AI and copyright, siding with artists who argue their work shouldn’t be scraped for training without compensation and calling for transparency about which works models were trained on. policy summary Her comments, which follow a $1.5B Anthropic settlement that set up a database of ~500,000 books with ~$3,000 payouts per author, suggest future UK rules may require provenance disclosure and licensing for training corpora—raising compliance stakes for model developers operating in or selling into the UK.
📊 Evals: IQ leaderboards and LLMs vs grad students
New/controversial benchmarks and tournaments. Today focuses on offline IQ tests and a market‑driven planning tournament where human coders beat LLM agents. Excludes training/optimizer papers.
“Vibe coded” LLM agents lose to grad CS students in strategic logistics tournament
A new benchmark tournament shows that 40 LLM‑written bidding and routing agents (“vibe coded” with natural‑language prompts) lose badly to 17 graduate CS students in a market‑driven logistics game, where companies bid for delivery tasks then plan vehicle routes to maximize profit. tournament summary Graduate‑written agents take the top five leaderboard spots, 33 of 40 LLM agents underperform even simple baseline heuristics, and many models pick poor A* heuristics or ignore extra vehicles in simplified sub‑tasks, despite emitting syntactically valid Java. ArXiv paper
The point is: standard coding benchmarks that only check unit tests miss this strategic failure mode, so if you’re deploying code‑gen agents into environments with competition, budgets, or long‑horizon planning, you should assume they’re still far from expert human performance unless you build explicit search, simulation and evaluation around them.
TrackingAI IQ board crowns Gemini 3 Pro on offline test while Grok 4 tops Mensa
TrackingAI’s new IQ leaderboard reports Grok‑4 Expert Mode at 136 on the public Mensa Norway puzzle set but only 126 on a held‑out "offline" test, while Gemini 3 Pro Preview scores a higher 142 on the offline test and 123 on Mensa, leading the overall offline ranking. IQ chart thread The offline portion uses unseen but stylistically similar pattern puzzles to reduce training‑data contamination, making its scores a more realistic proxy for genuine abstract reasoning than legacy public tests. Rundown summary
For engineers, the gap between Mensa and offline scores is the key signal: models can still overfit or memorize web‑exposed benchmarks, yet retain strong non‑verbal reasoning when probed with fresh items, so you should treat headline "IQ" numbers as task‑dependent and avoid reading them as a single scalar for intelligence.
Language Model Council proposes multi‑LLM “democratic” judging for subjective tasks
The Language Model Council (LMC) paper introduces a benchmark where a panel of 20+ LLMs collaboratively design test prompts, answer them, and then act as a jury to rank each other’s responses on subjective skills like emotional intelligence and advice‑giving, instead of relying on a single judge model such as GPT‑4o. paper highlight The process yields a leaderboard with scores and confidence intervals derived from many cross‑model comparisons, aiming to average out intra‑model bias and better reflect performance on “soft” tasks that lack crisp ground truth. council diagram
For teams who currently lean on one LLM‑as‑judge to score creative writing, interpersonal tone, or persuasion, LMC is a reminder that those scores may largely reflect the judge’s own style; a small local council of heterogeneous models, even if informal, can give more stable rankings for model selection and fine‑tune evals.
💼 Capital and distribution: funding and usage shifts
Enterprise and capital signals: a major vision startup raise and concrete usage/adoption metrics. Excludes ChatGPT anniversary metrics (feature) and creative model defaults (covered under media).
FT data shows Gemini app closing gap with ChatGPT on downloads and engagement
Financial Times charts based on Sensor Tower estimates show Google’s Gemini mobile app rapidly catching up to ChatGPT in monthly global downloads, with Gemini rising toward the tens of millions of installs per month and narrowing the gap to ChatGPT’s ~100M range by late 2025. ft usage charts The same analysis reports that Gemini users now spend slightly more time per visit (around 7–8 minutes) than users of rival chatbots, while Alphabet’s market cap edges toward $4T on investor expectations that Gemini can materially defend Google’s search and cloud franchises.
For builders, this is a distribution signal: even if you still prefer OpenAI or Anthropic models for certain workloads, Gemini’s growing consumer footprint means more end users will experience AI through Google surfaces first (Android, Chrome, Workspace), which can tilt which ecosystems get first‑class integrations, default buttons and data access. For leaders and analysts, it reinforces that the AI assistant market is not locked up by one vendor; Google’s ability to convert search traffic and Android reach into Gemini usage makes it a durable competitor, which should affect partnership strategy (who you integrate with by default) and risk modeling around platform dependence.
- If you ship consumer apps, test how your flows feel with Gemini as the default assistant on Android and Chrome.
- If you sell B2B AI products, expect more customers to ask "does this plug into Gemini?" next year as Google leans on this usage story in enterprise sales.
Black Forest Labs raises $300M Series B to scale FLUX visual models
Black Forest Labs, maker of the FLUX image models, closed a $300M Series B at a reported ~$3.25B post-money valuation, saying its systems now serve "millions" of users each month and power production workflows on major creative platforms. funding announcement The company’s blog highlights FLUX as one of the most-used open image families on Hugging Face and notes integrations with services like Fal.ai, Replicate and Together for enterprise serving. funding blog For AI engineers and product teams this means FLUX is likely to remain a well-funded, independent alternative to proprietary image stacks from OpenAI, Google and Midjourney, and its bet on "visual intelligence" (generation, perception, memory, reasoning in one stack) suggests more unified APIs rather than one-off diffusion checkpoints. For leaders and analysts, a $300M round at multi‑billion valuation is a clear signal that investors still see large upside in foundation vision models even as the frontier-model race for text is getting crowded, and that creative tooling, design, and marketing pipelines will continue shifting toward model-agnostic, API‑driven image infrastructure rather than single closed platforms.
🎬 Creative stacks: Nano Banana Pro workflows and new video contenders
Heavy creative/media chatter: NB Pro prompting techniques, depth/canny guidance demos, and looming model launches. Includes Perplexity’s default gens; excludes enterprise adoption metrics.
Perplexity makes Nano Banana Pro and Sora 2 Pro its default generators
Perplexity quietly switched its default generation stack to Google’s Nano Banana Pro for images and Sora 2 Pro for video across both Perplexity and its Comet agent, at least for paying users. perplexity default update For builders, this means a lot of “out of the box” Perplexity content will now inherit Nano Banana’s photorealism and Sora 2’s long‑form video style, without any prompt changes. It’s a strong signal that a third‑party search startup currently rates these as better cost/quality trade‑offs than DALL·E, Imagen, or Midjourney in its workflow.
If your team relies on Perplexity or Comet in production, it’s worth re‑checking safety filters, brand style prompts, and latency assumptions, since you’ve effectively been migrated to a new creative stack without touching your own code.
Kling teases Omni launch as Whisper Thunder stays atop video leaderboards
Kuaishou’s KlingAI is teasing an “OMNI launch week” under the tagline “Omniverse begins,” signaling some kind of omni‑modal or all‑in‑one video model arriving this week. omni teaser text
At the same time, the mystery video model “Whisper Thunder (aka David)” remains at the top of Artificial Analysis’s text‑to‑video leaderboard, edging out Google’s Veo 3 and Kling 2.5 Turbo on ELO, and some observers now speculate Whisper Thunder is in fact a Kling model under a different label. whisper kling claim
Following Whisper model, which first flagged Whisper Thunder’s sudden rise, this week’s hints suggest Chinese video labs are not just catching up but quietly planting state‑of‑the‑art models in public evals—something teams choosing between Veo, Sora, and open contenders will want to watch very closely.
Nano Banana Pro prompting guide codifies depth maps and cinematic edits
A detailed community guide for Nano Banana Pro is making the rounds, turning scattered prompt tricks into a playbook for controllable, film‑style edits. nbp guide mention You get patterns for turning chaotic scenes into clean story images, specifying lens, grain, and color timing, plus advice on how much detail helps vs hurts. guide article Following up on control guidance that showed NB Pro acting like a ControlNet, people are now demoing it respecting explicit depth maps for retakes instead of hallucinating geometry. depth map demo Others use simple prompts like “as if this were a film with orange and teal cinematic color grading, lighting, and film grain” to restyle real photos and even Google Maps views into convincing stills. map film example The same stack is showing up inside Adobe Firefly’s Gemini 3 workflows, where creators are pushing it into full sci‑fi storyboards from a single description, tightening the loop from idea to shot list. firefly storyboard demo For anyone wiring NB Pro into their own product, this guide is a good shortcut to sensible defaults and a reminder that depth/canny inputs massively increase repeatability over raw text.
EngineAI’s T‑800 teaser points to a new hyper‑realistic video model
EngineAI dropped a short teaser for its upcoming “T‑800” model, promising a launch in three days and showing a Terminator‑style endoskeleton head rendered so cleanly that viewers argued over whether it was CGI or live‑action. realism reaction
There are no specs yet, but the clip suggests the team is chasing the same hyper‑real, metal‑and‑lighting heavy shots where models like Sora 2, Veo 3, and Whisper Thunder tend to show their limits. If T‑800 really is as good as the promo, it could become a go‑to specialist for VFX‑like material even if it’s not a generalist video workhorse.
For creative engineers, the main takeaway is that the “stack” for serious video work keeps getting more fragmented: you may soon be routing prompts between Veo for everyday scenes, Sora for long narratives, Kling/Whisper for physics‑heavy shots, and T‑800 for close‑up metal and texture—making orchestration and evals more important than betting on a single model.
🗂️ Extraction & retrieval: spreadsheets to people search
Concrete data workflows: auto‑structuring messy Excel and open‑source people search with LangGraph/RAG. Mostly practical extraction; excludes browser‑automation agent harnesses (covered under agents).
LlamaSheets agent automates messy Excel-to-table ETL for finance data
LlamaIndex quietly shipped LlamaSheets, a specialized agent that takes messy financial Excel workbooks and restructures them into clean 2D tables ready for analysis, targeting workflows where accountants and analysts currently do hours of manual ETL. LlamaSheets launch
The demo shows LlamaSheets ingesting unstructured spreadsheets, normalizing layouts, and outputting analysis-ready tables, which is especially useful for financial statements that aren’t “database‑shaped” and often block downstream BI or modeling. The team is pitching it for repetitive accounting and finance ETL tasks, where you can hand off the structure discovery and reformatting to an agent instead of custom scripts or one‑off macros. LlamaSheets page
Free 6-day "Improving RAG" course focuses on absence blindness and query design
Jxnlco launched a free 6‑day email series on RAG optimisation, promising concrete patterns for fixing issues like absence blindness, bad query segmentation, and brittle multimodal retrieval. Improving RAG course The syllabus covers tuning retrieval and routing (e.g., smart question segmentation and query typing), turning RAG into a data-generating loop, and handling messy data types so you can actually measure and improve your system instead of tweaking prompts blindly. For teams already shipping RAG apps, this looks aimed at lifting recall and answer quality without immediately jumping to large model fine-tuning. Improving RAG page
PeopleHub open-sources AI-powered LinkedIn people search and research
LangChain highlighted PeopleHub, an open-source "LinkedIn intelligence" stack that lets you run natural‑language people search and auto-generated research reports on public profiles. PeopleHub overview
Built with LangGraph 1.0.1, Google Gemini 2.0, Bright Data scrapers, Redis, and Postgres, it turns prompts like “10 AI engineers in Israel” into structured candidate lists plus AI-written due-diligence summaries. The project leans heavily on multi-tier caching, claiming 70–90% cost reduction on repeat or batched profile lookups, which matters if you’re building recruiting, sales-intel, or expert-finder tools on top of noisy web data. PeopleHub repo
Guidance: strong generic re-rankers often beat per-domain fine-tuning
A short thread argues you don’t always need to fine-tune re-rankers per domain, because good re-rankers tend to work across FAQs, legal docs, e‑commerce catalogs, and financial content. Re-ranker advice The key point is that domain nuance—user profiles in e‑commerce, jurisdiction hierarchies in law, entity filters in finance—should often live in your retrieval schema and filters rather than in a bespoke re-ranker for each vertical. For people designing RAG systems, this nudges you toward investing more in indexing strategy, metadata, and filtering logic, and treating the re-ranker as a mostly reusable component instead of a proliferation of narrowly tuned models.
🧪 New/open models: OCR and speech coverage expansion
Smaller but relevant model items: an open VLM for OCR tasks and Meta’s broad multilingual ASR push. Few frontier LLM releases today; mostly applied perception models.
Meta unveils open ASR stack covering 1,600+ languages
Meta researchers introduced an open speech recognition system that already supports more than 1,600 languages, with tooling designed so the coverage can keep growing as new data arrives. meta asr summary Rather than a single monolith, the stack packages models, recipes, and language resources so outside teams can extend or adapt it—explicitly targeting under‑resourced languages that never make it into commercial ASR APIs.
For engineers, this is a big deal if you’ve been stuck with English‑first or "top 50" language support: it should become much easier to prototype voice interfaces, transcription, and search for local markets without building an entire ASR pipeline from scratch. For AI leaders, the move also raises the competitive bar on how open speech infrastructure should be; once a 1,600‑language baseline exists in the wild, it gets harder to justify narrow, proprietary-only offerings that ignore most of the world’s languages.
Tencent’s HunyuanOCR 1B VLM sets new open benchmark for OCR
Tencent’s Hunyuan team released HunyuanOCR, a ~1B‑parameter vision–language model specialized for OCR that beats larger models on several benchmarks and wins the ICDAR 2025 DIMT small‑model track. dl_weekly mention The architecture couples a ViT encoder with a lightweight language head and MLP adapter so it can handle text spotting, document parsing and information extraction in a single end‑to‑end system, rather than stitching classic OCR with downstream LLMs. ArXiv paper For builders this is one of the first compact, open VLMs that’s actually competitive with commercial APIs: it reportedly sets a new state of the art on OCRBench among models under 3B parameters, while staying small enough to run on commodity GPUs. That makes it a realistic candidate for on‑prem document workflows (invoices, forms, passports) and multilingual UI text extraction where sending data to closed clouds is a problem. Analysts should watch whether teams swap out proprietary OCR stacks for HunyuanOCR + thin business logic, because that’s the kind of quiet replacement that changes cost structure in fintech, logistics, and e‑gov stacks without a lot of marketing noise.